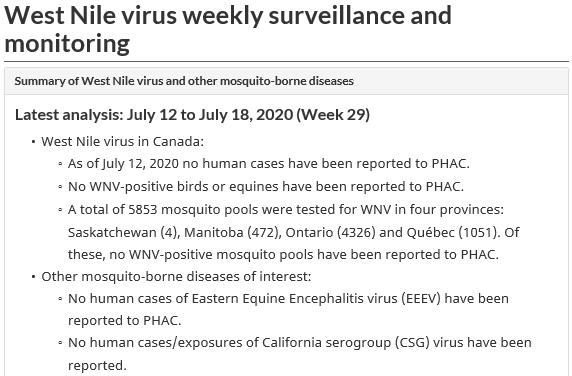
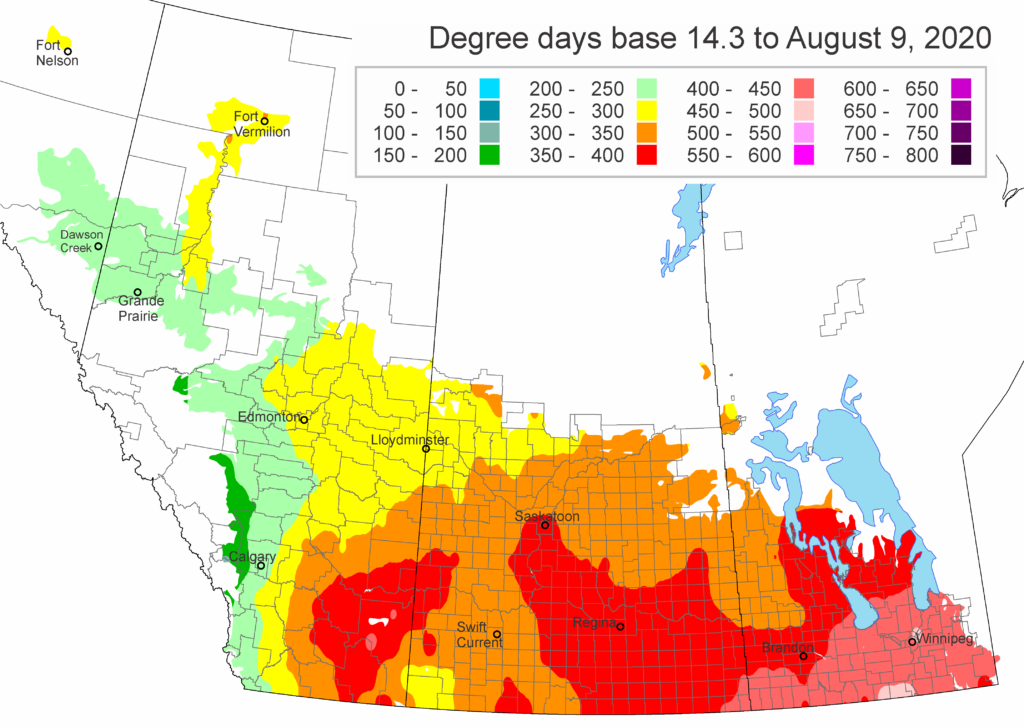
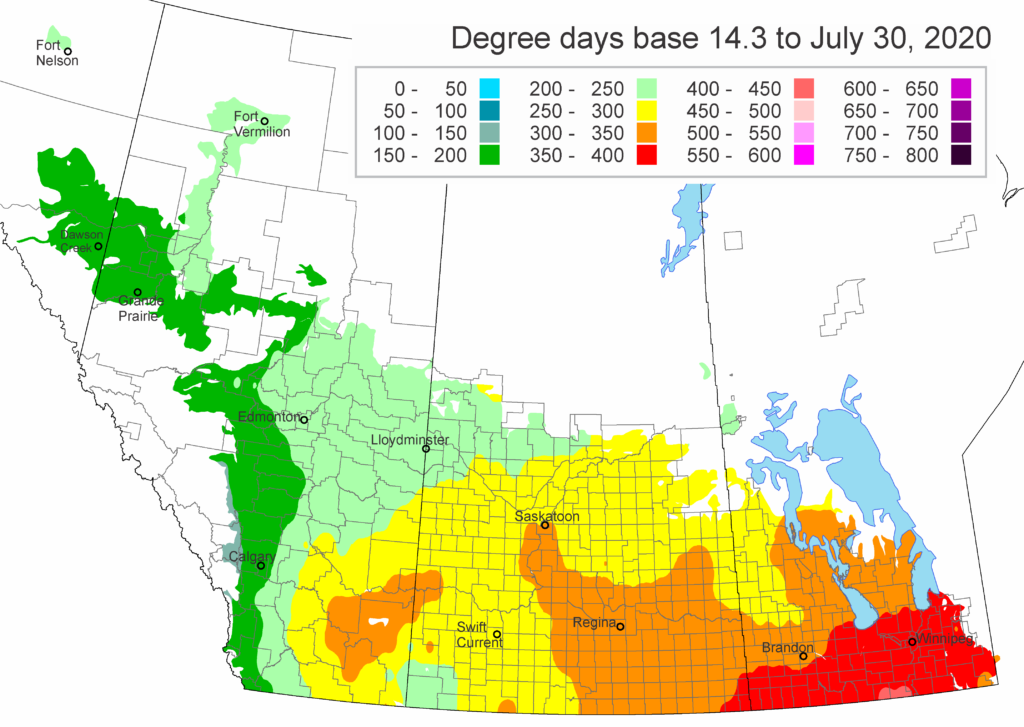
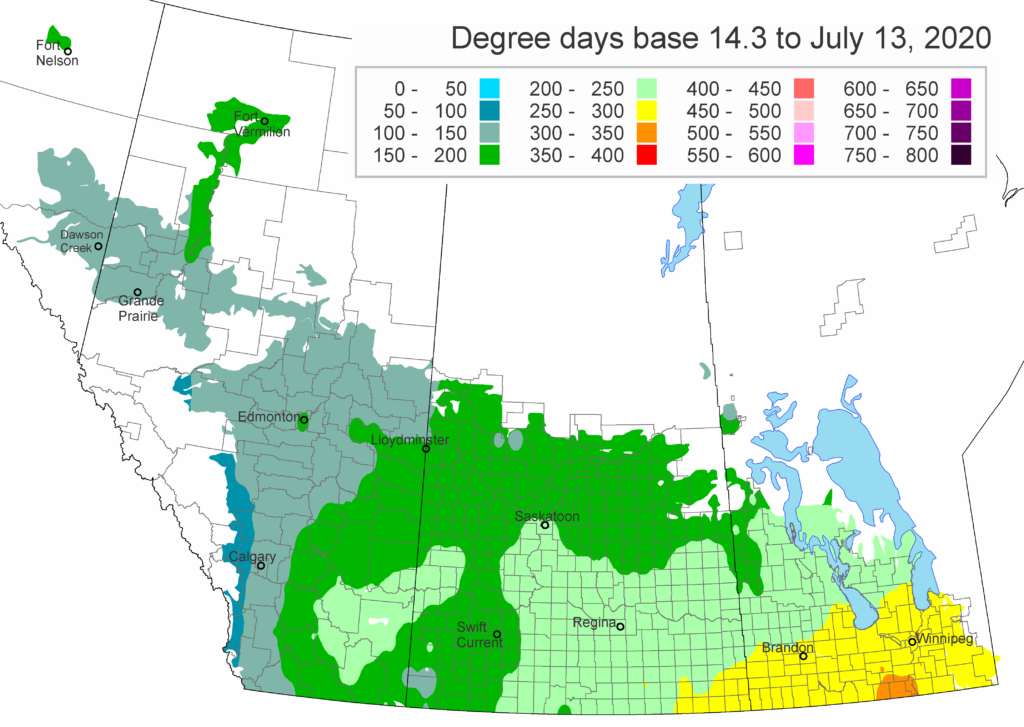
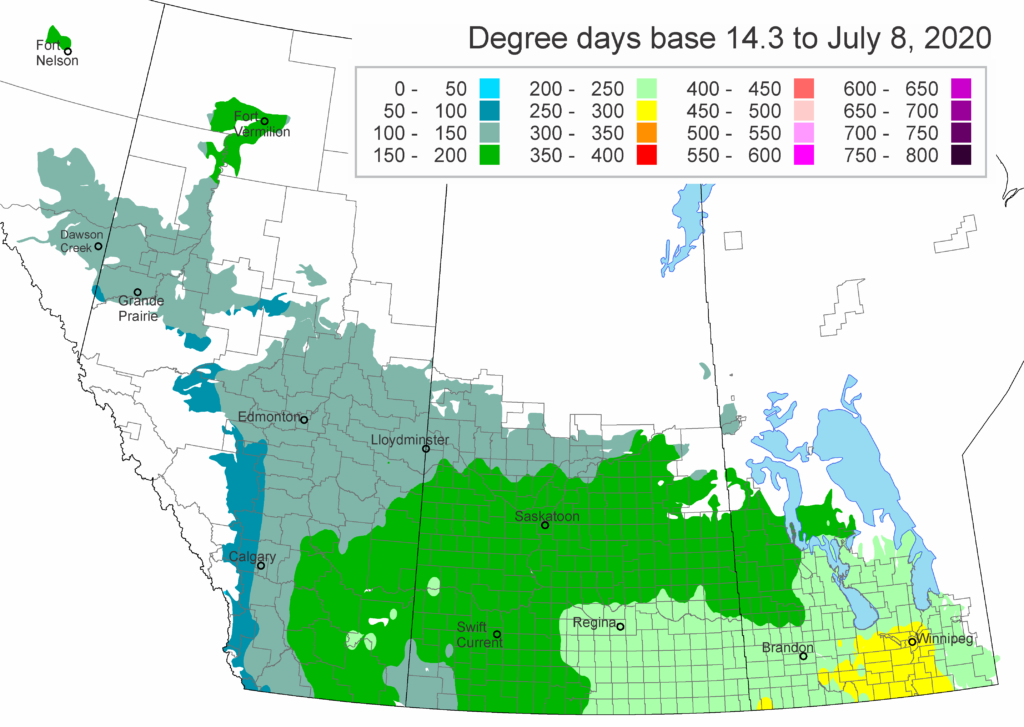
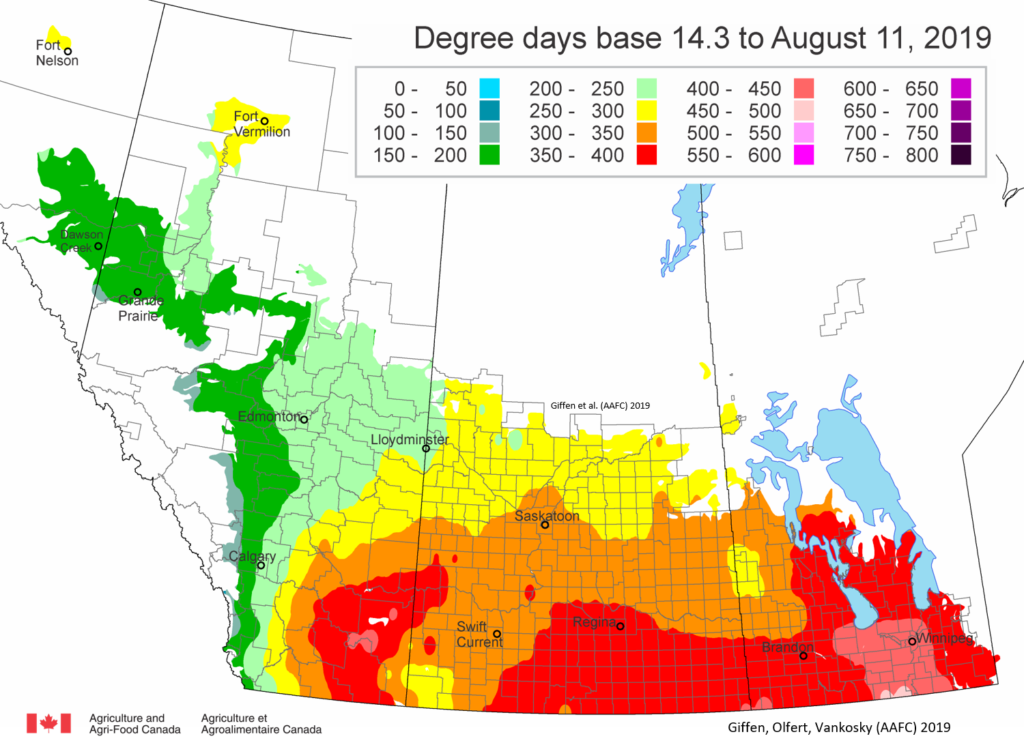
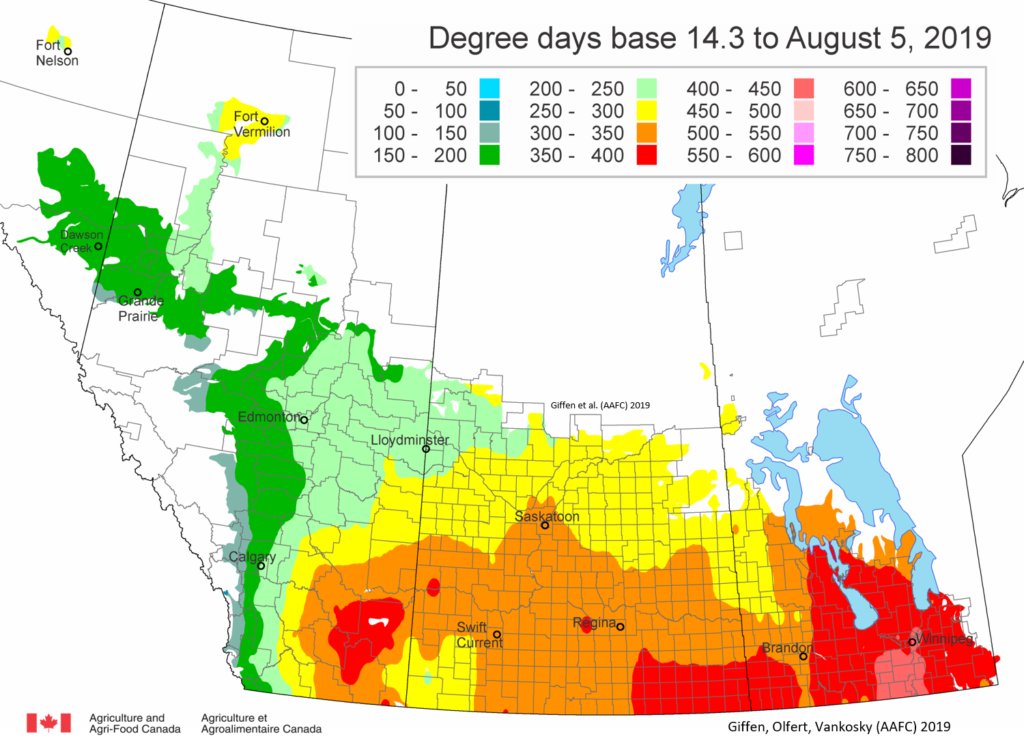
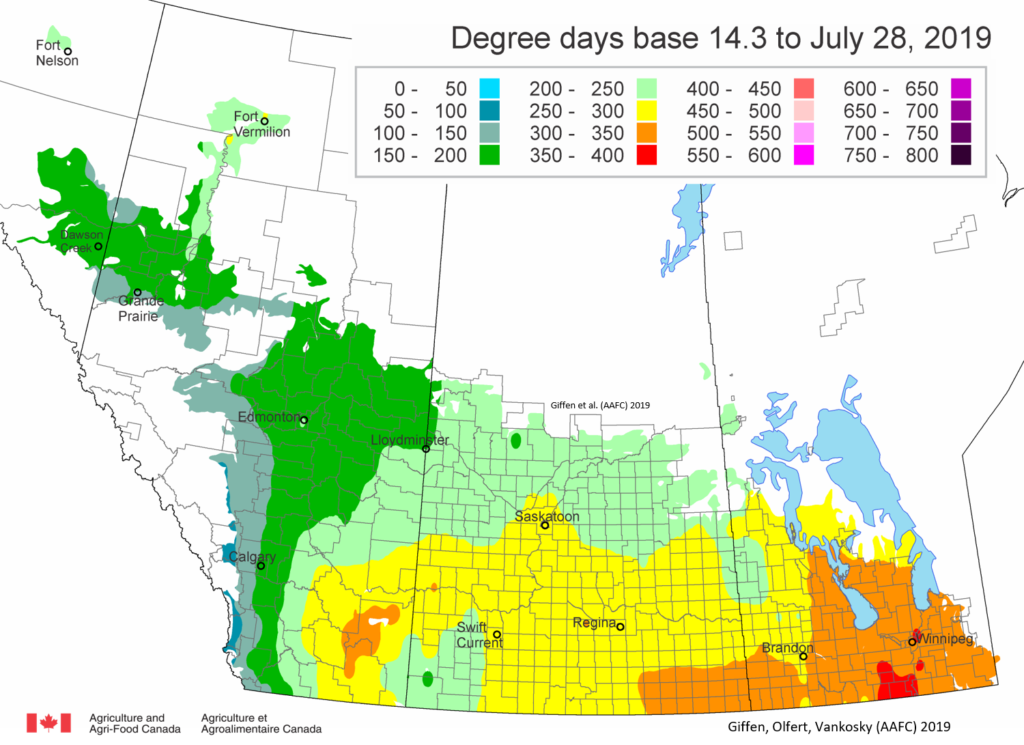
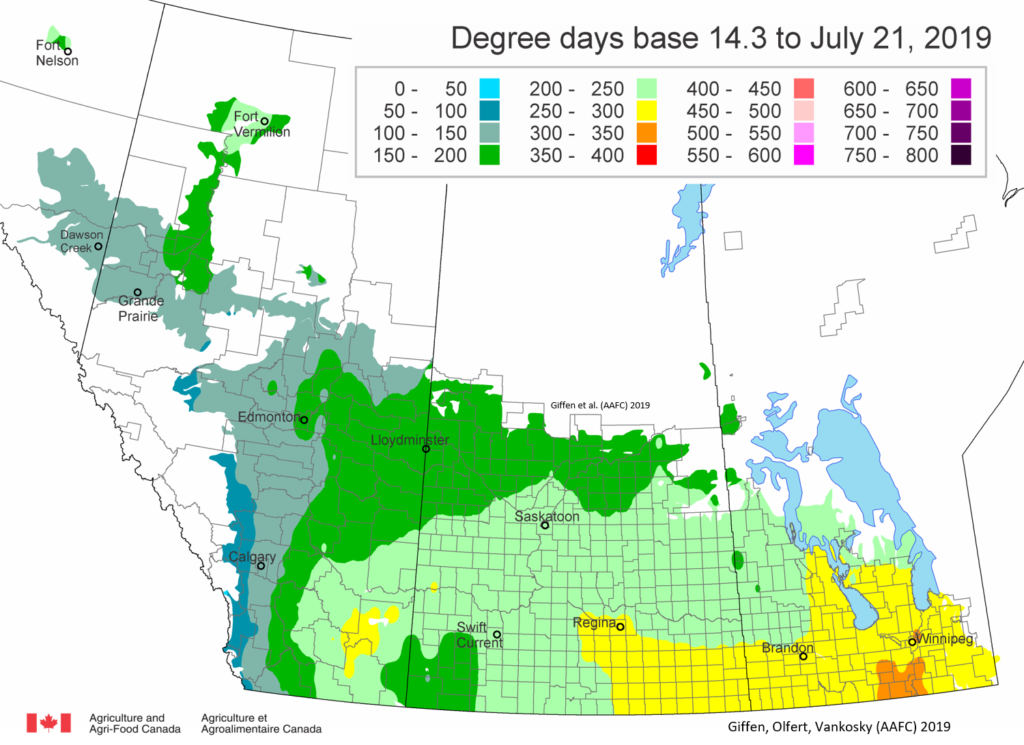
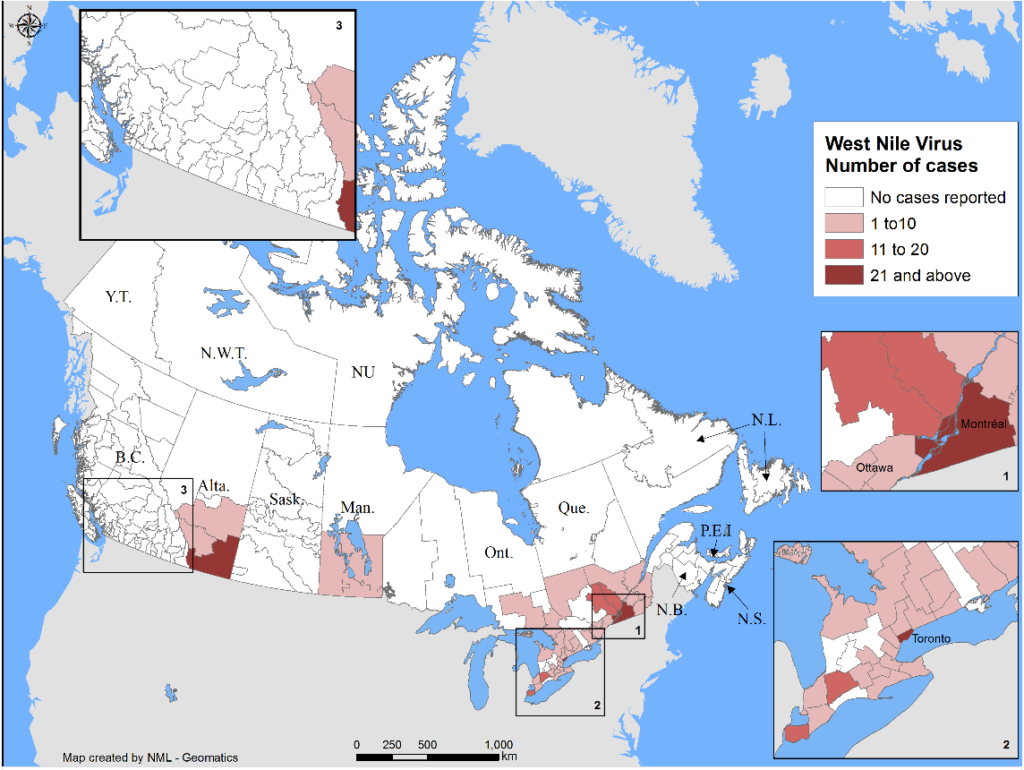
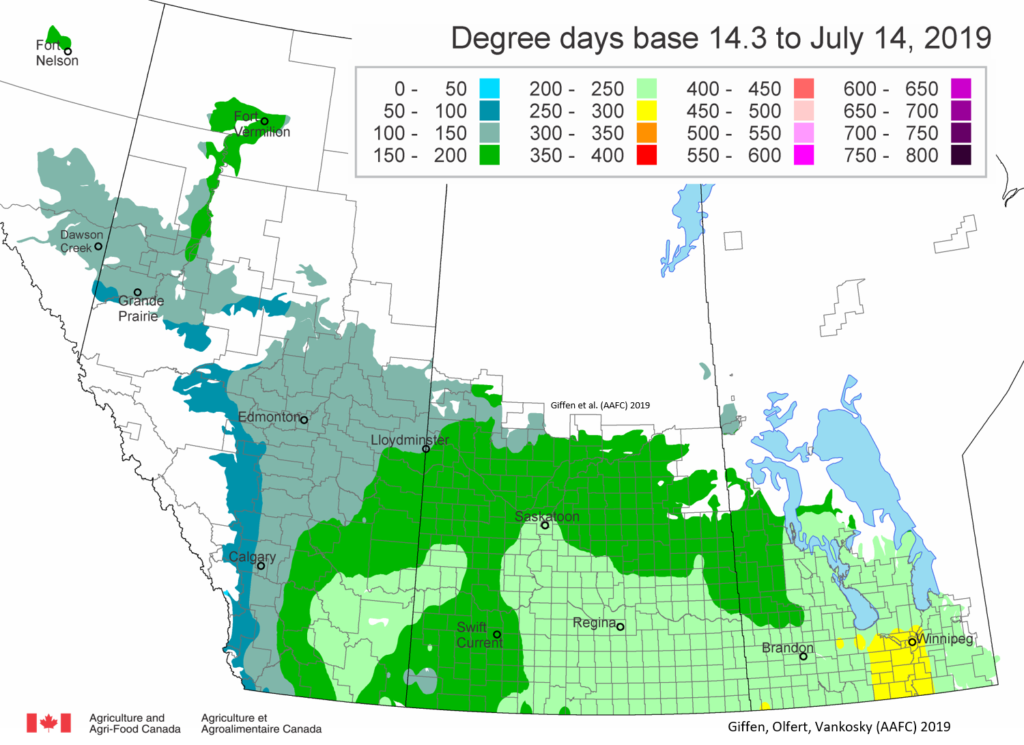
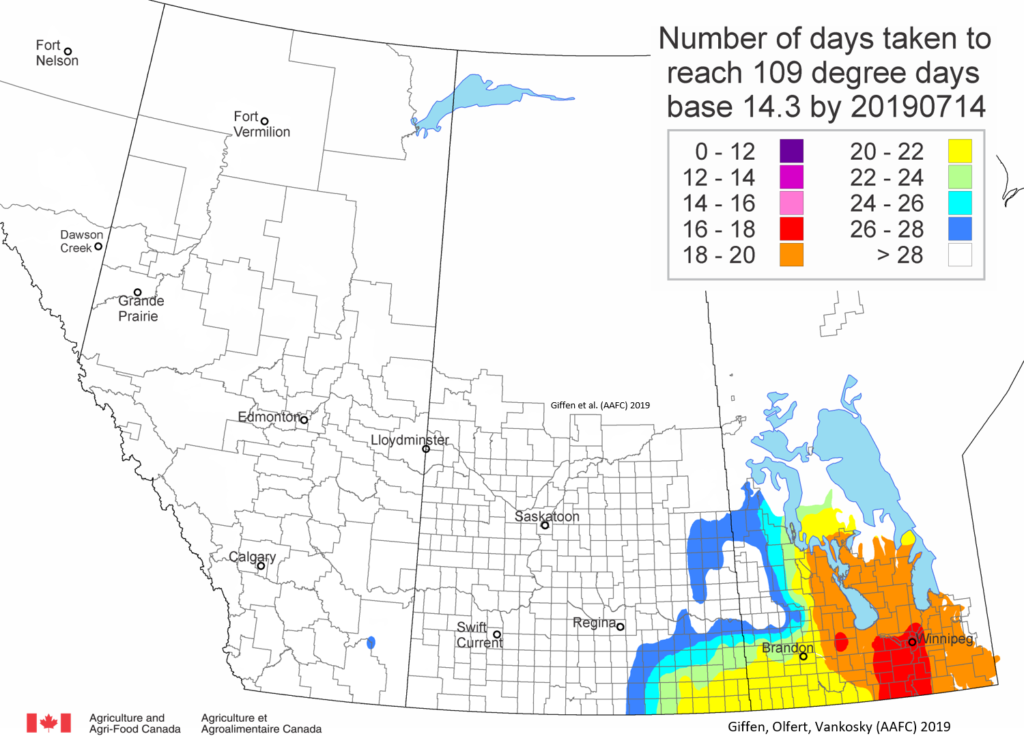
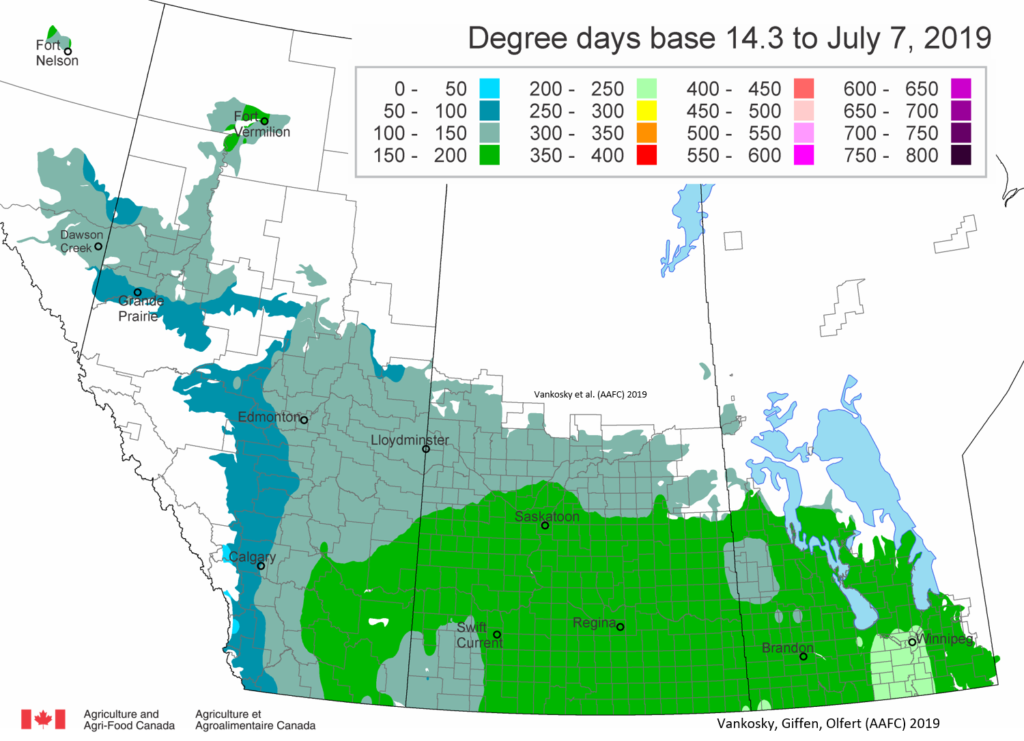
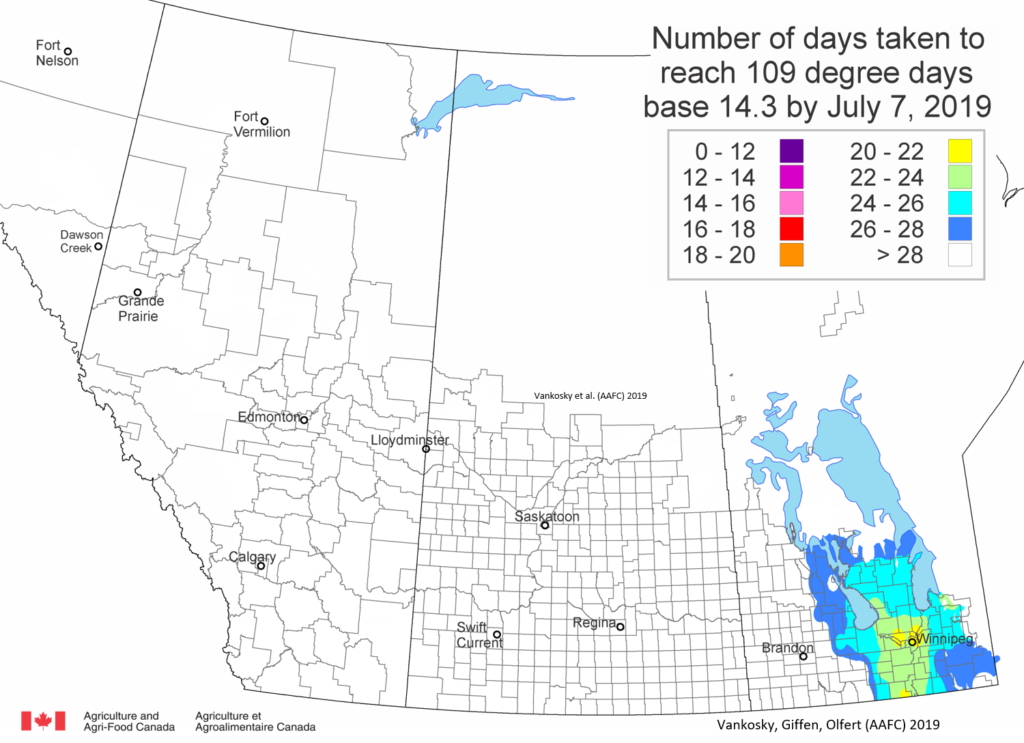
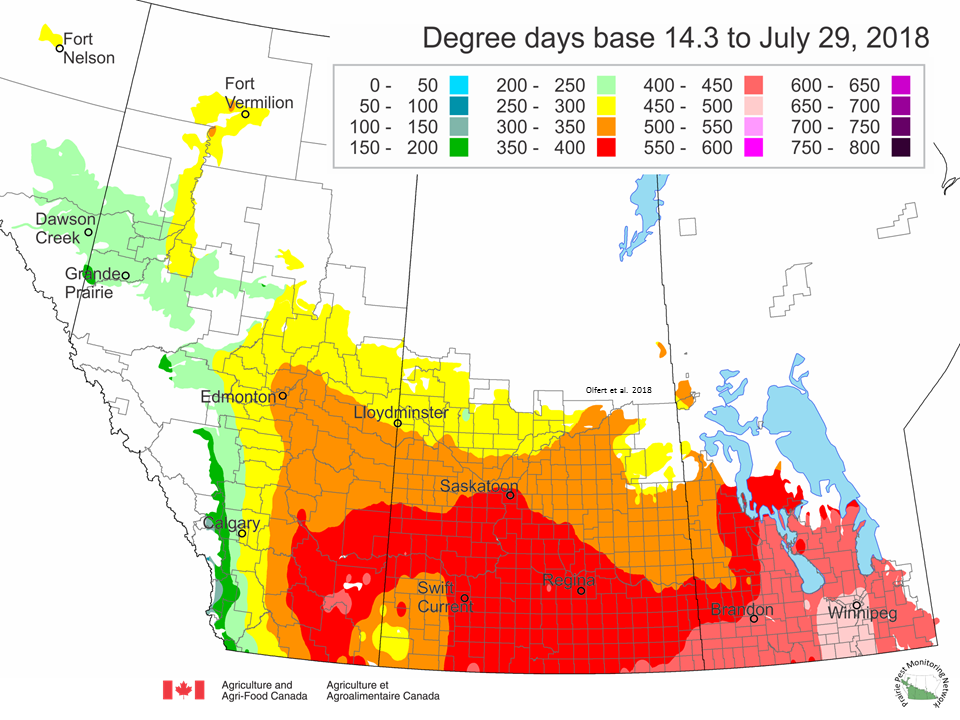
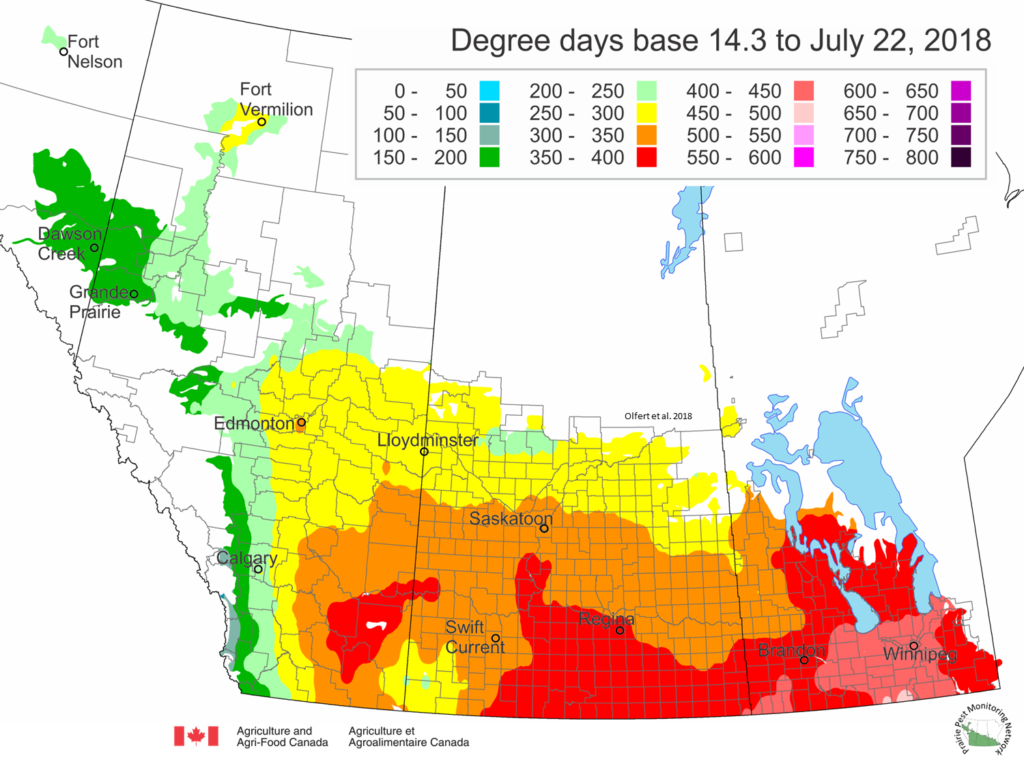
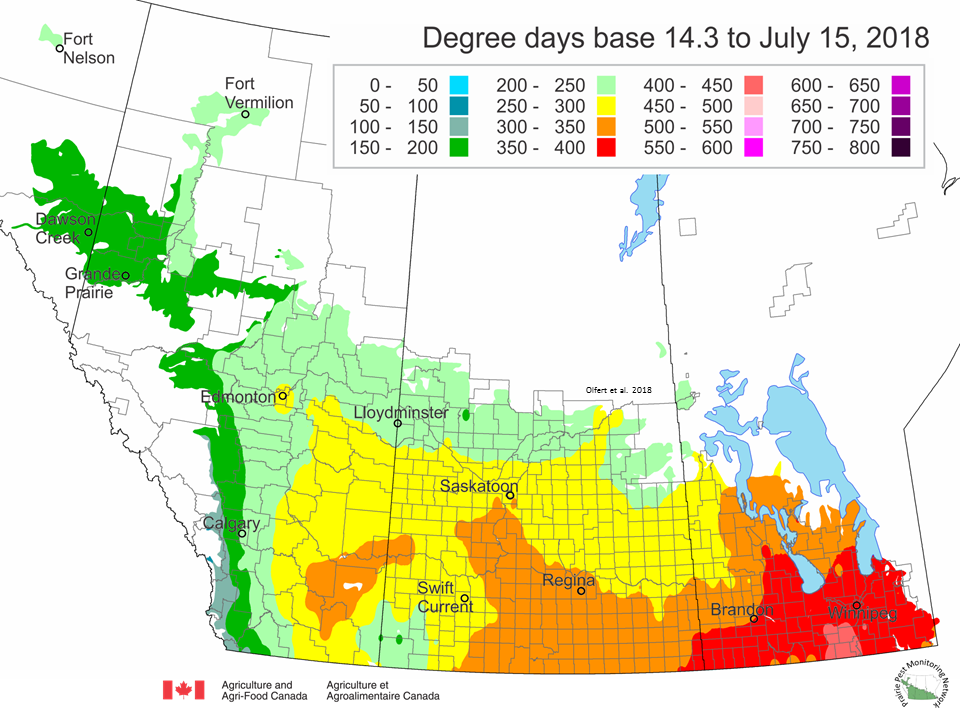
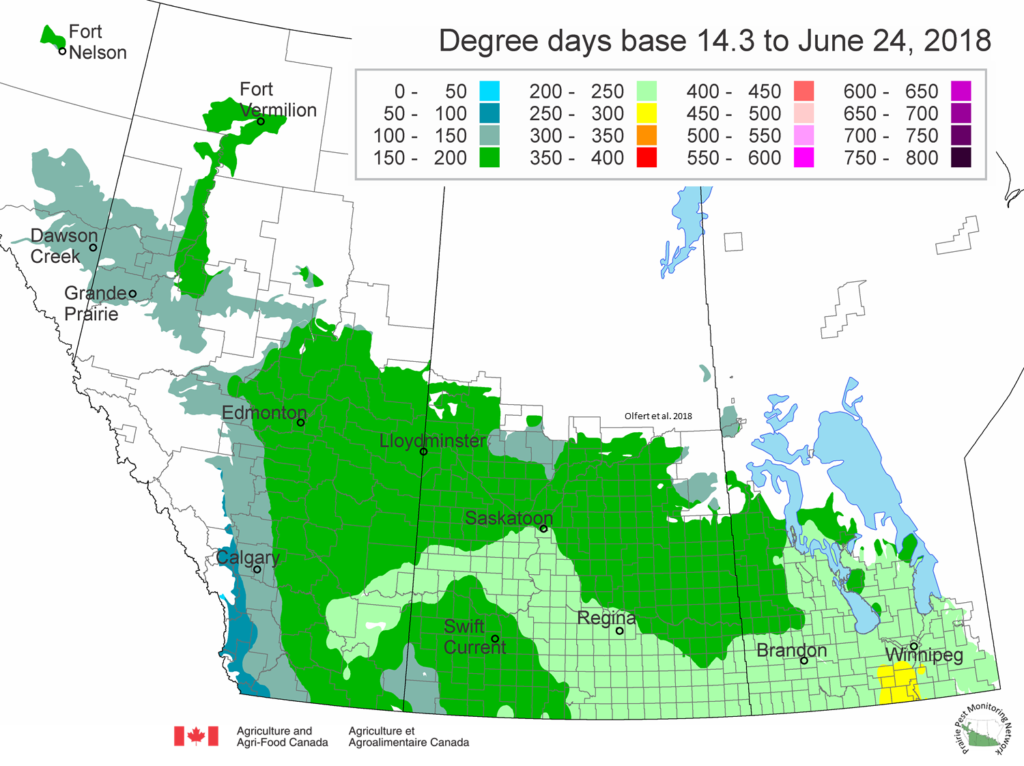
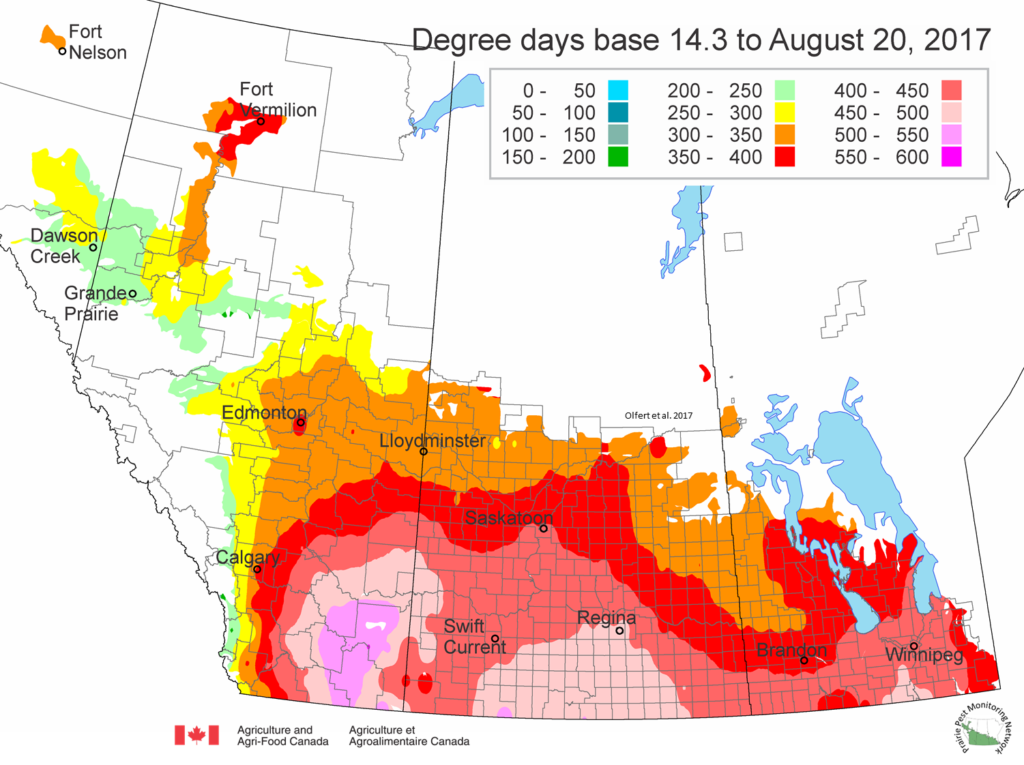
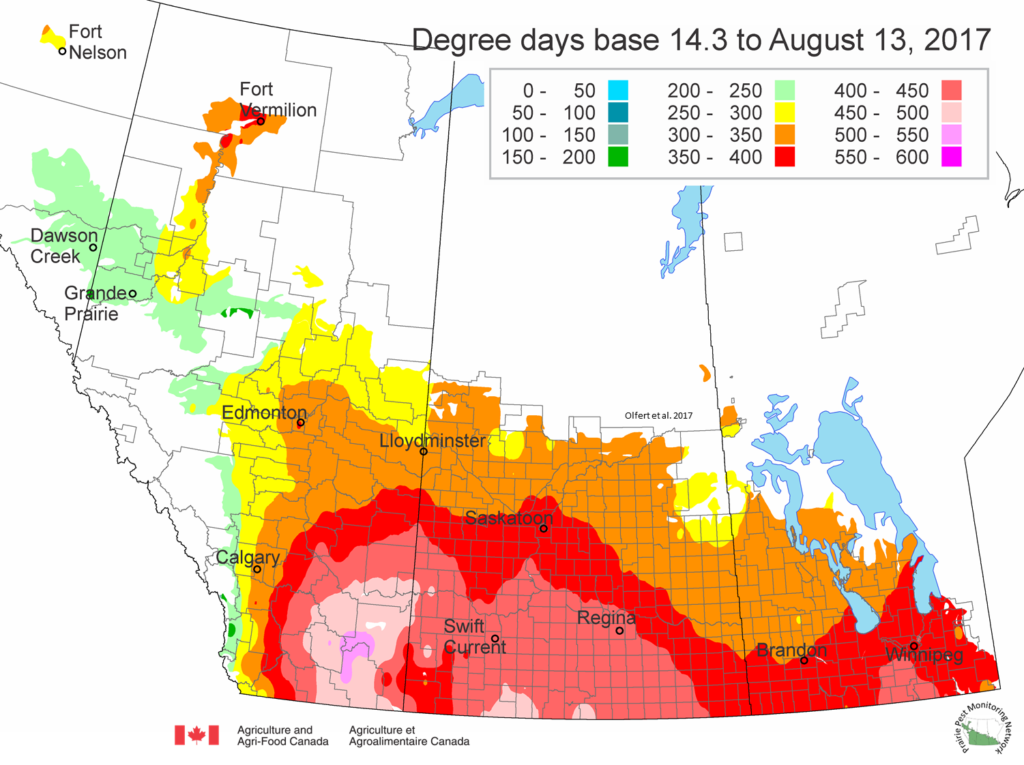
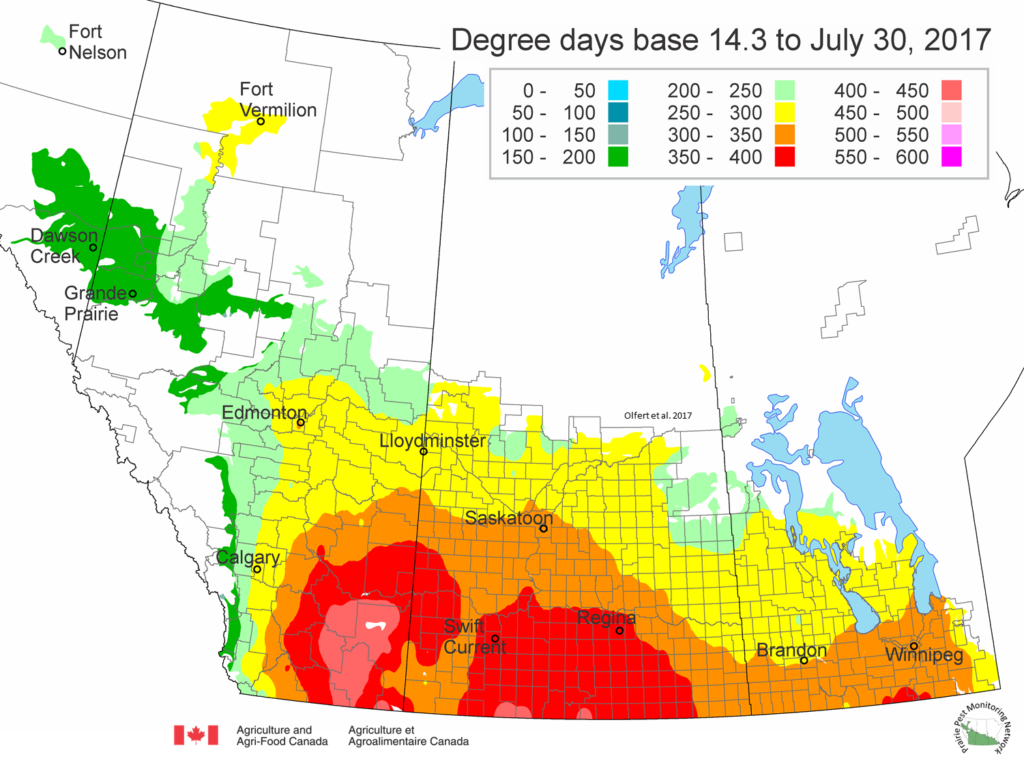
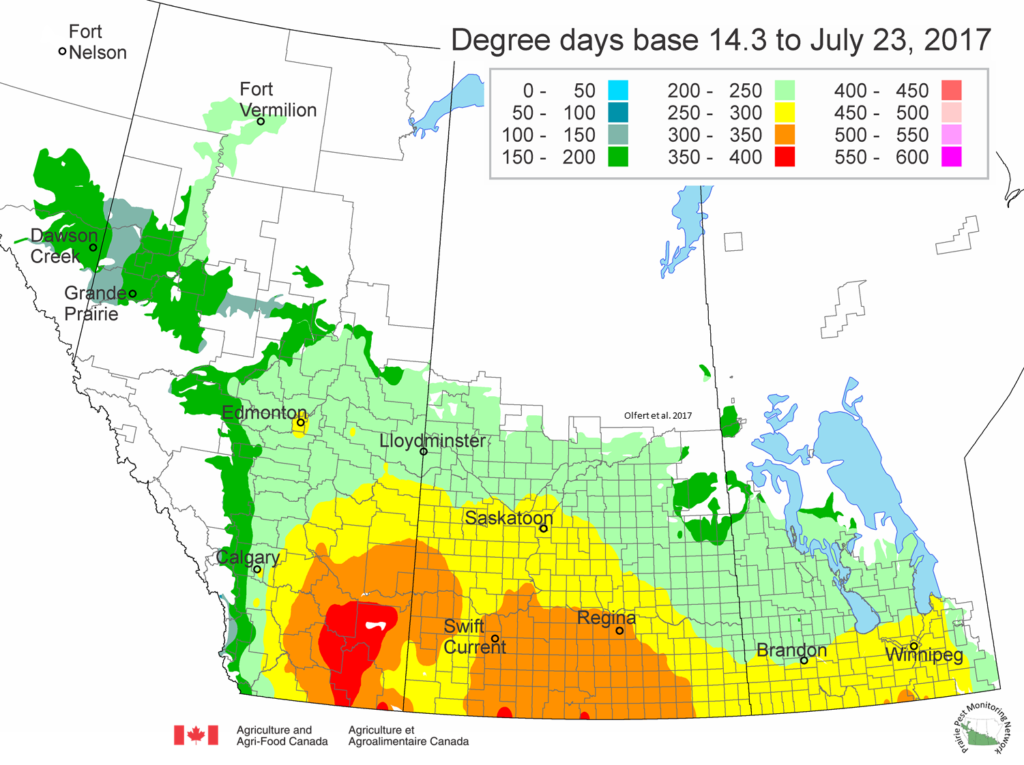
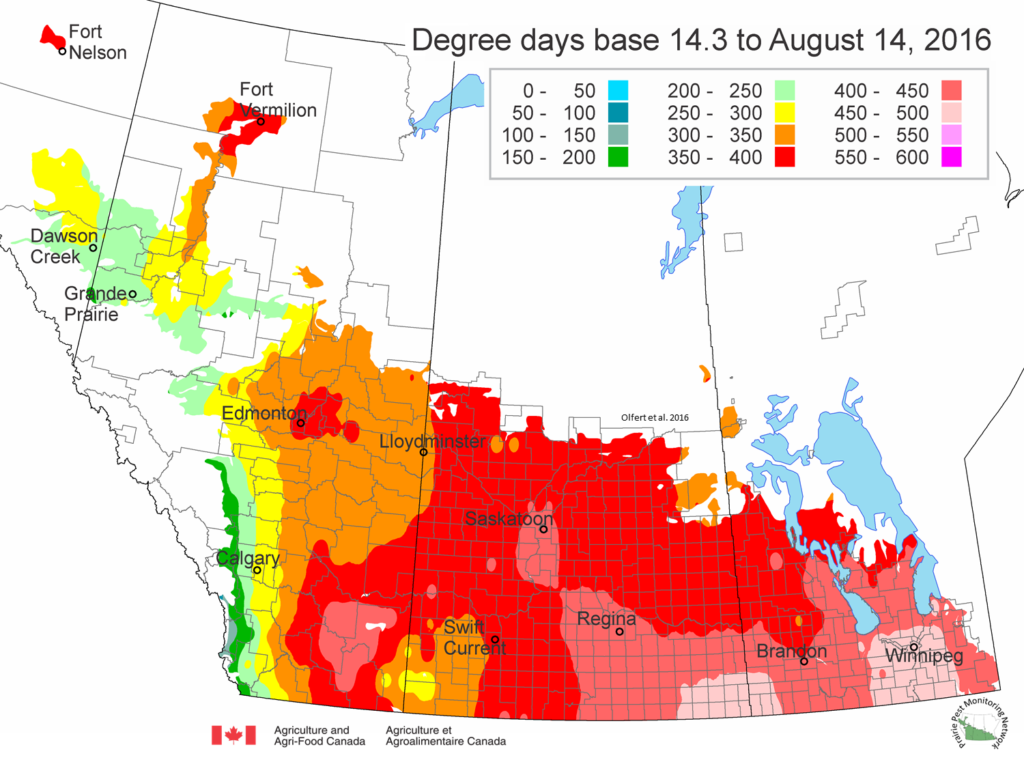
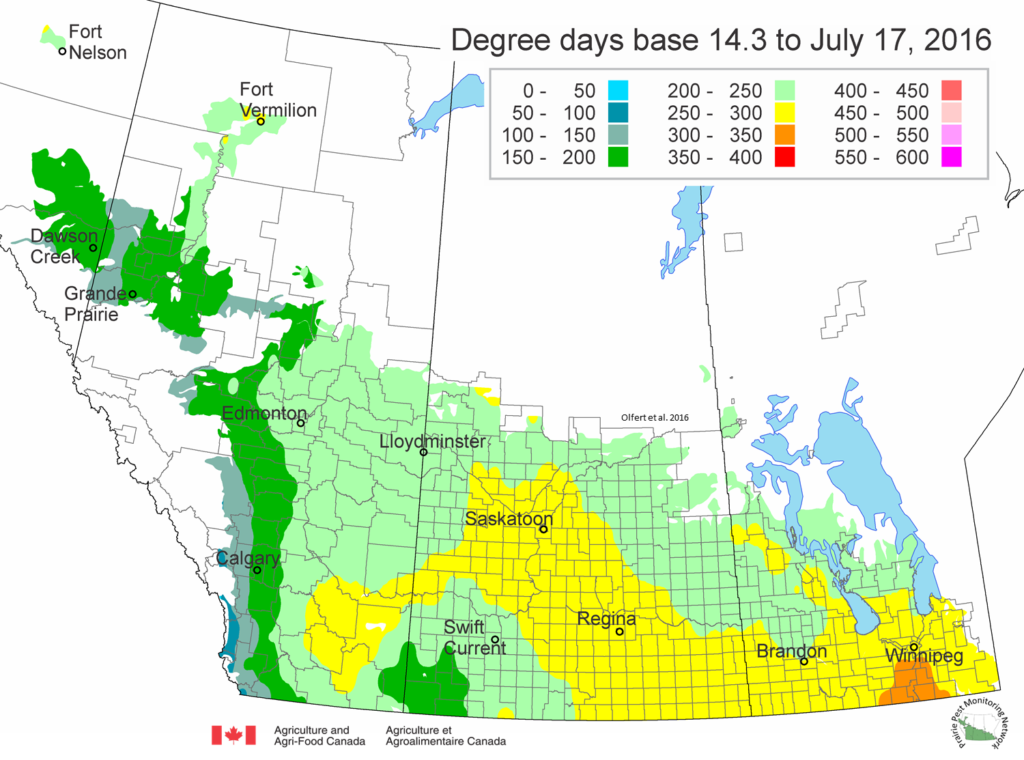
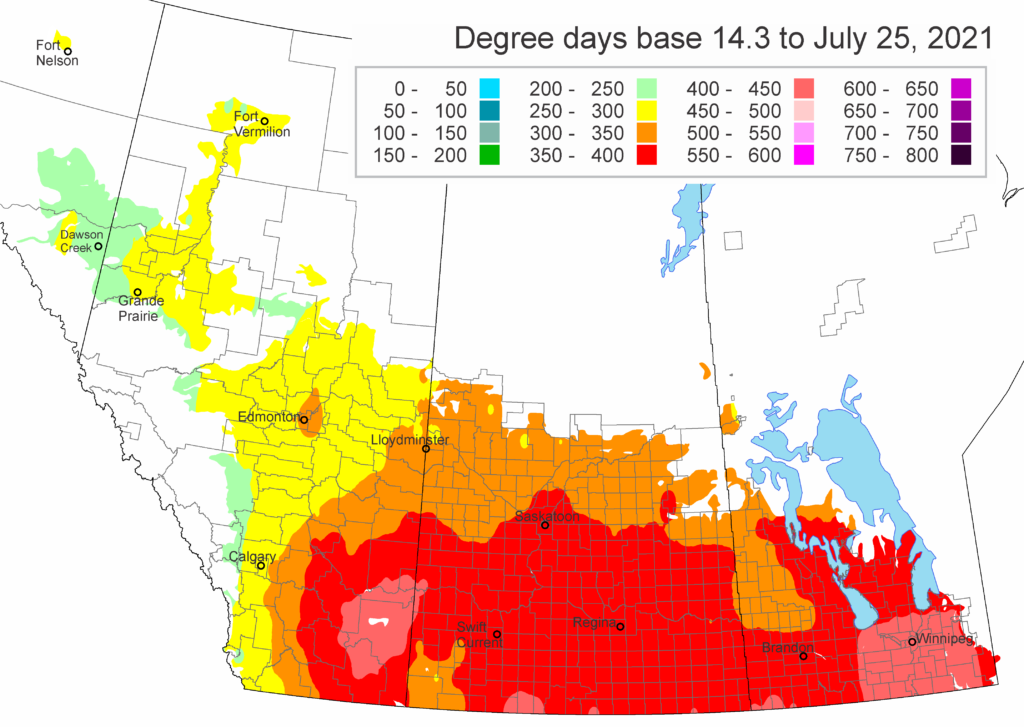
The following is offered to help predict when Culex tarsalis, the vector for West Nile Virus, will begin to fly across the Canadian prairies. This week, regions most advanced in degree-day accumulations for Culex tarsalis are shown in Figure 1 but the unusual heat across the prairies greatly accelerated mosquito development!
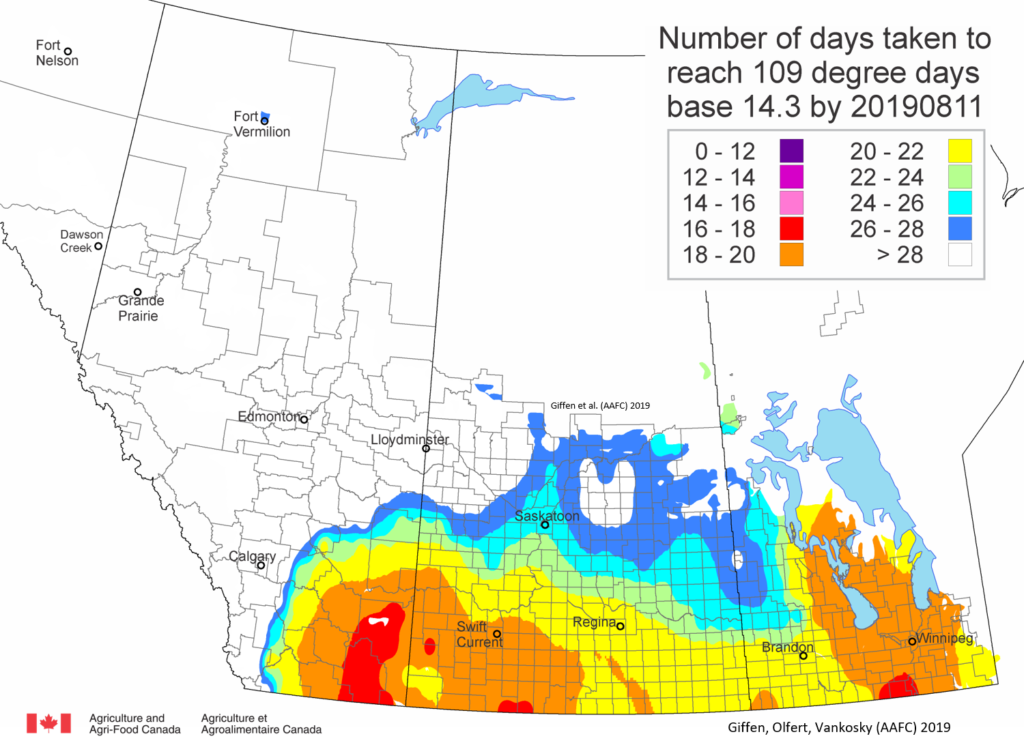
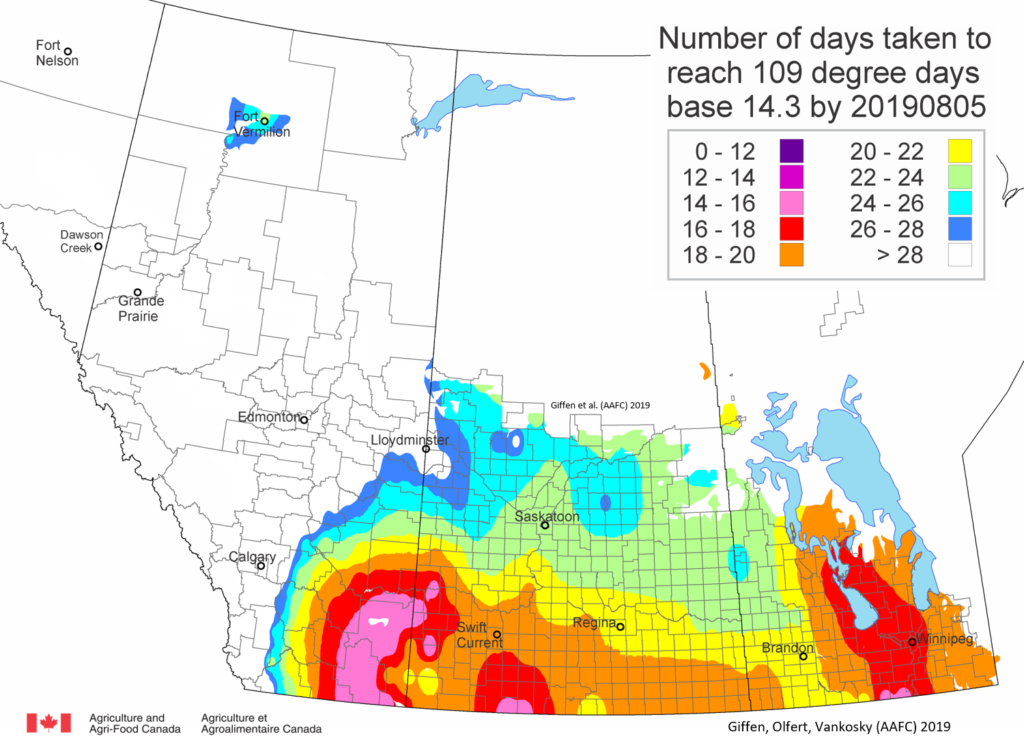
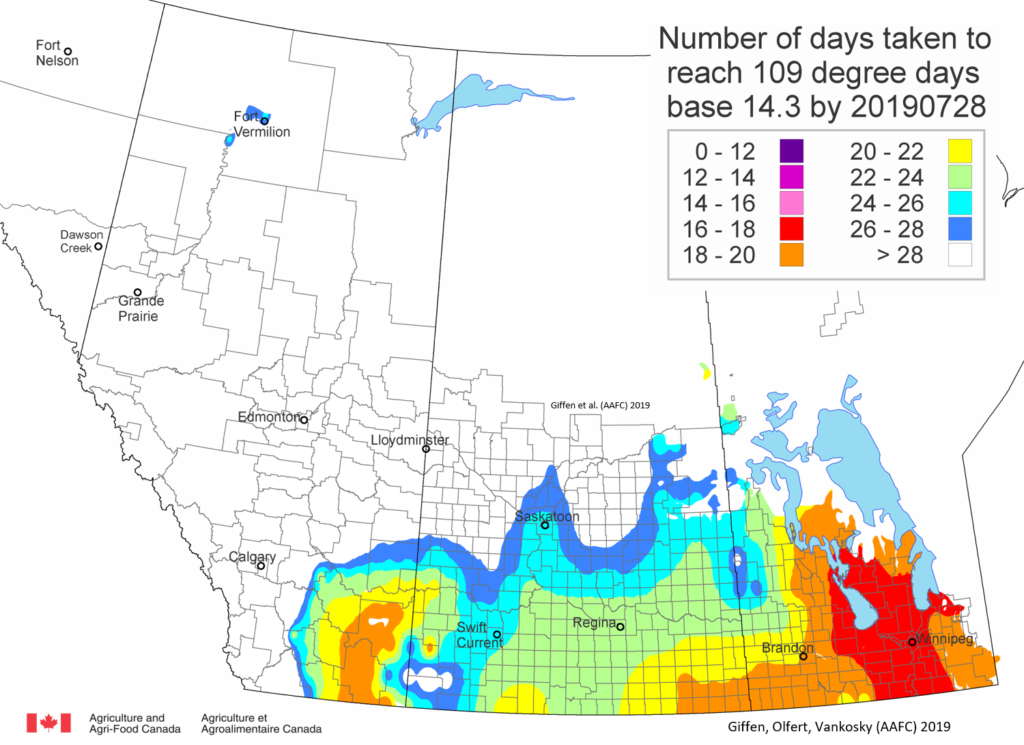
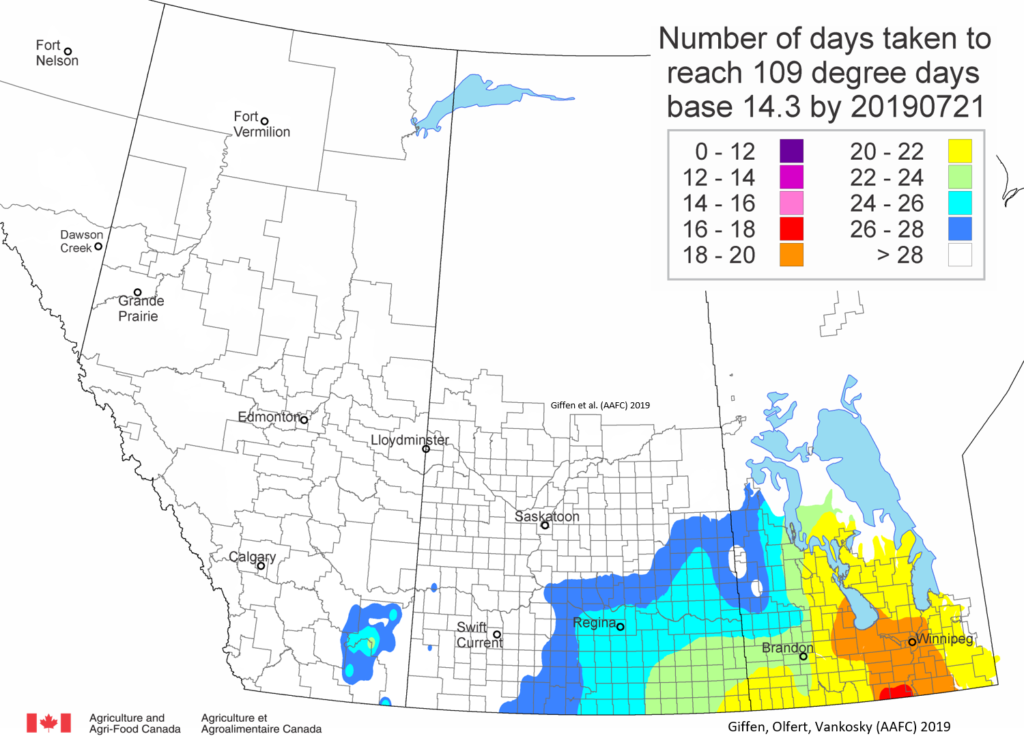
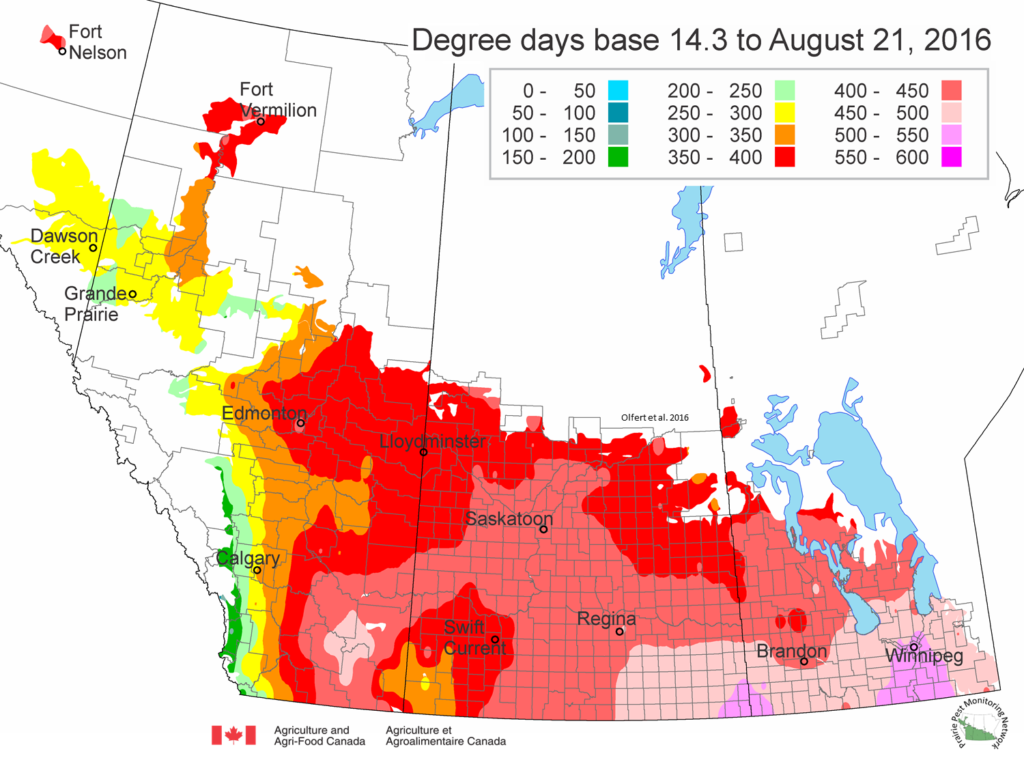
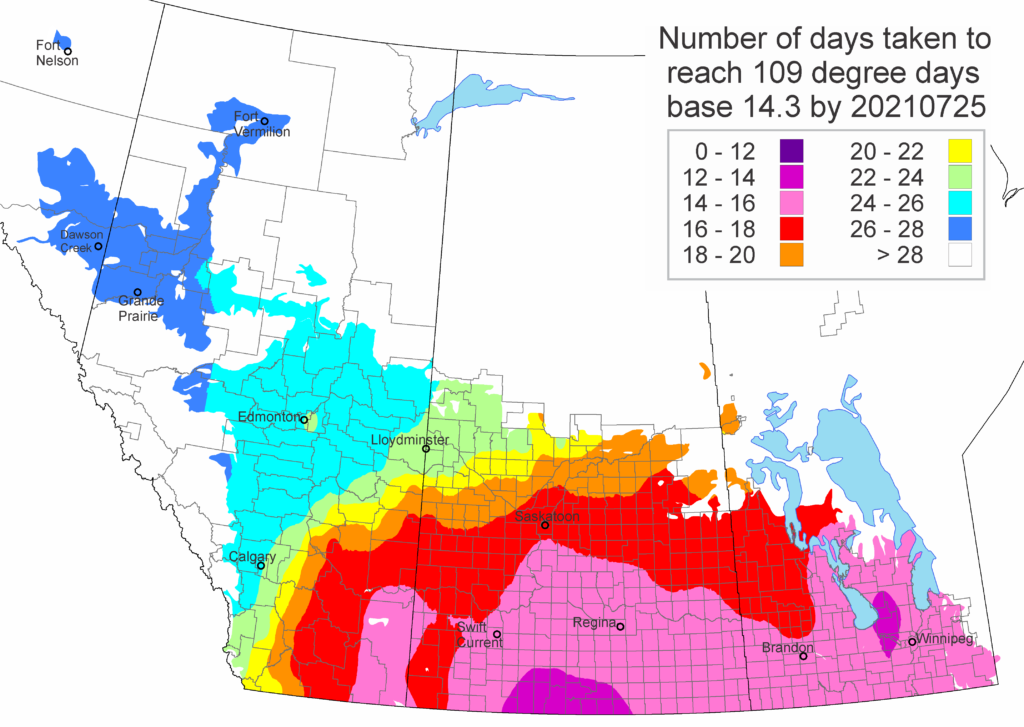
As of July 25, 2021 (Fig. 1), C. tarsalis development has now reached the point that adults are predicted to be flying across the south of the prairies from Manitoba to Alberta. Outdoor enthusiasts falling within areas highlighted red (i.e., areas that have accumulated sufficient heat accumulation for C. tarsalis to emerge) should wear DEET to protect against WNV! Because of the continued high temperatures, areas highlighted yellow or orange in the map below (as of July 25) should also start to use DEET this week! IF C. tarsalis is present in an area where WNV is active, it may take as little as 14 days for adults to become fully infective with the current warm weather (Fig. 2).
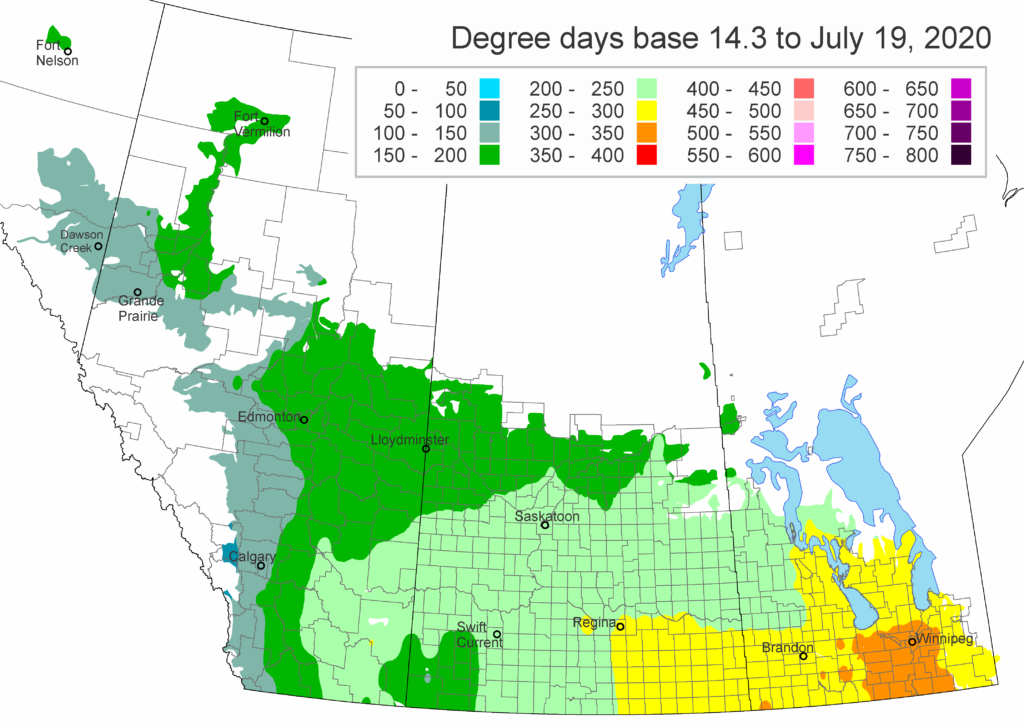
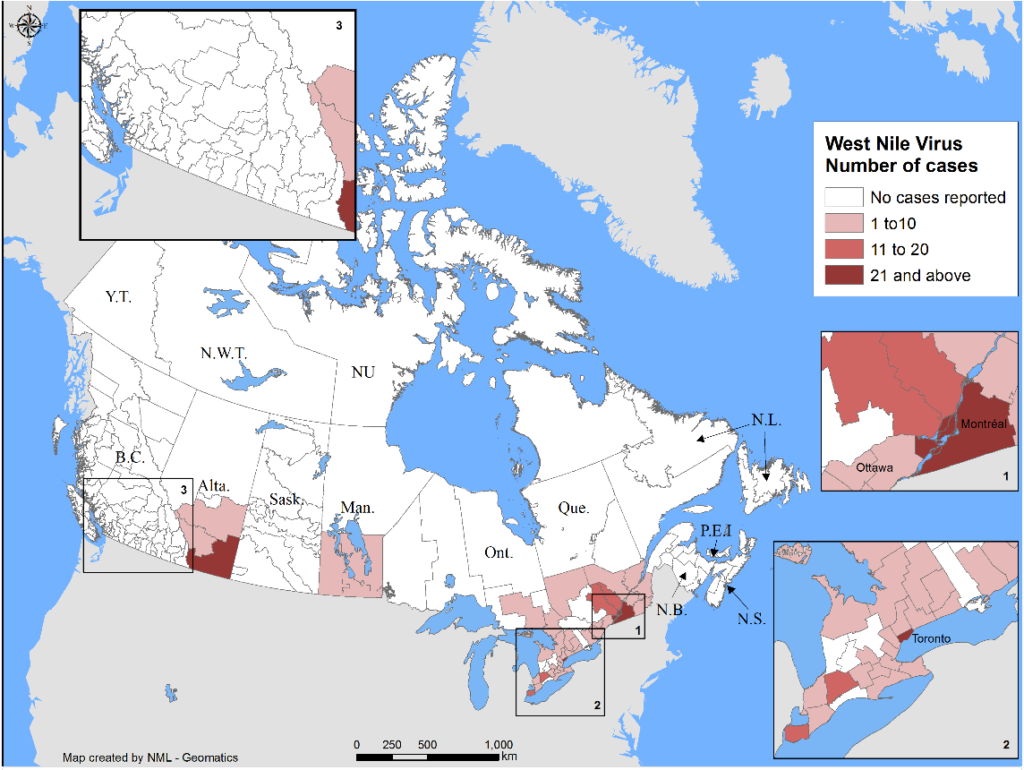
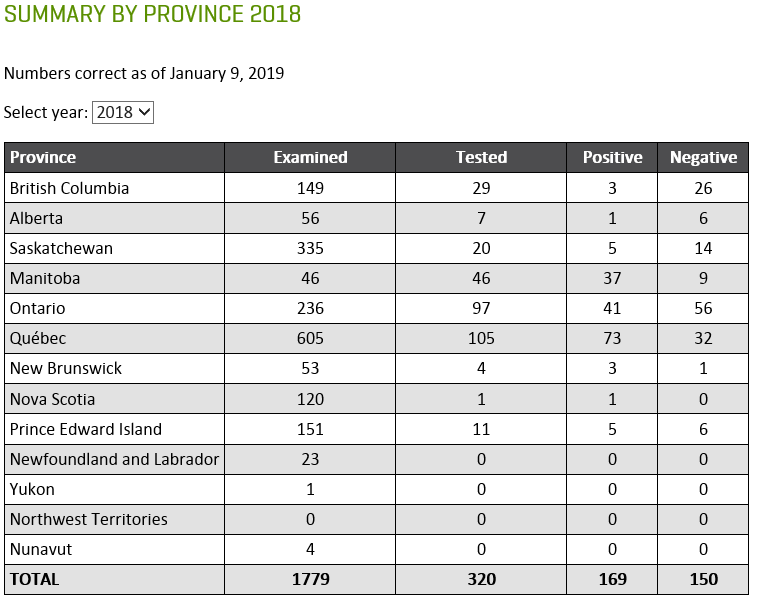
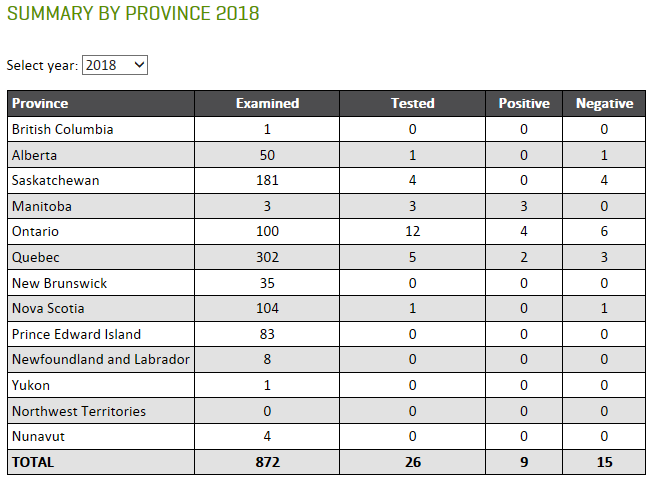
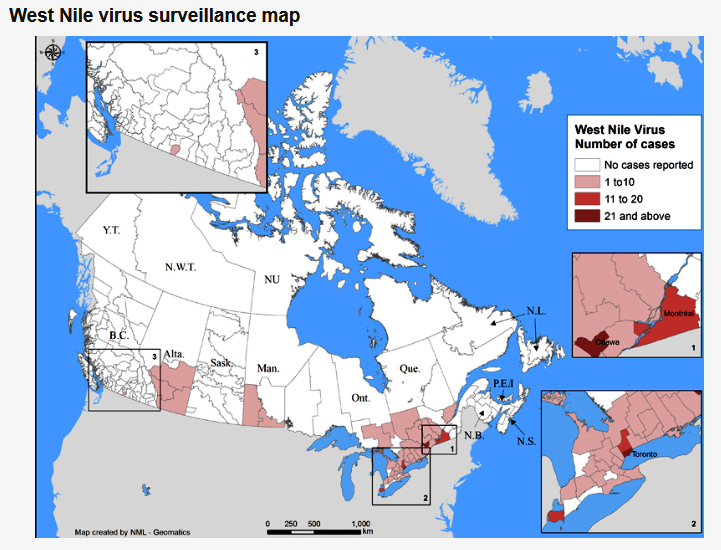
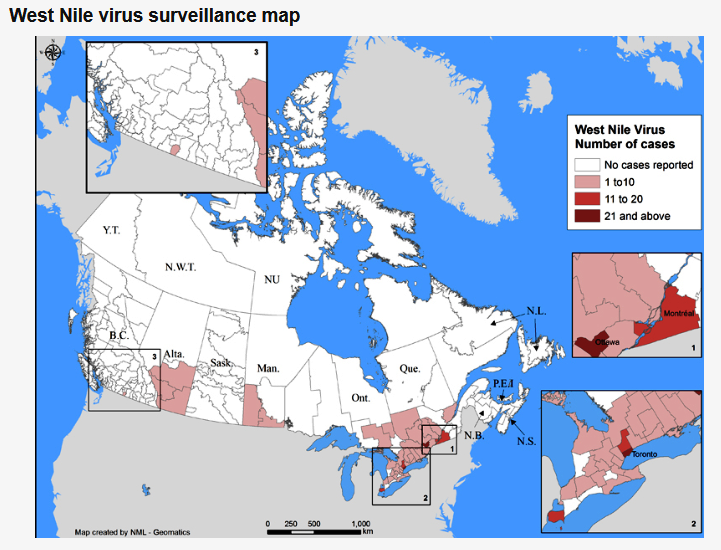
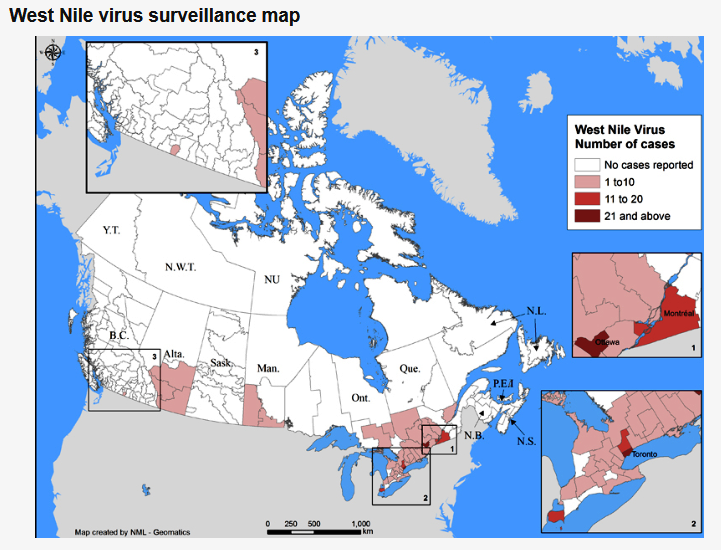
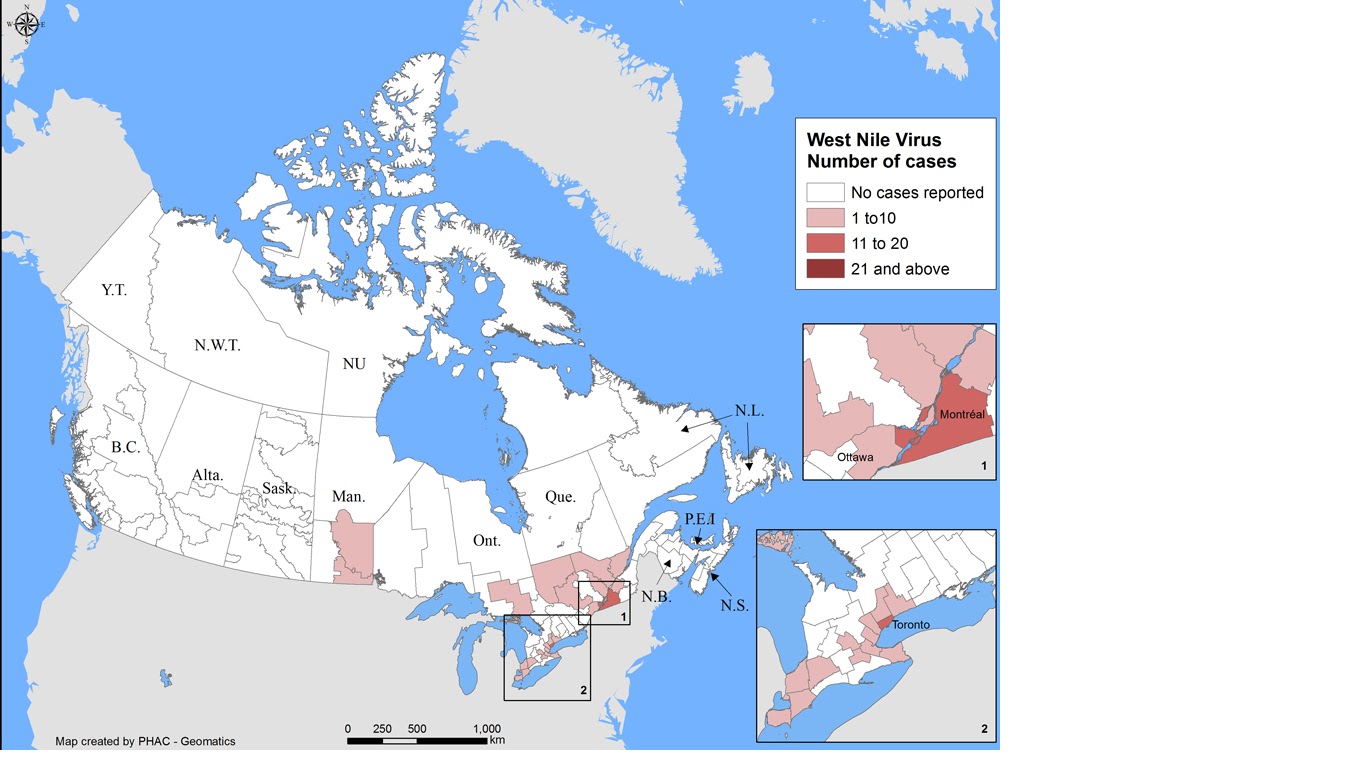
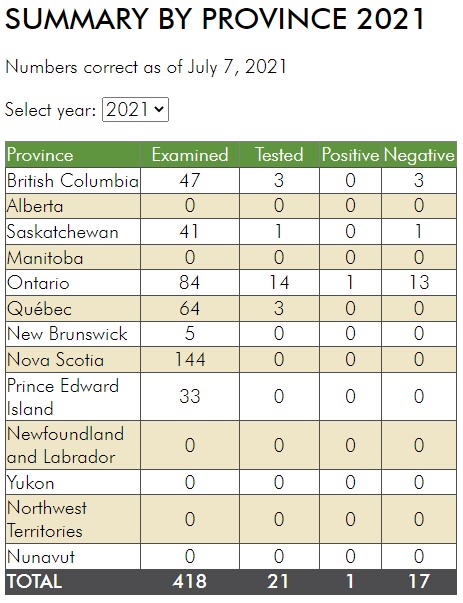
The Public Health Agency of Canada posts information related to West Nile Virus in Canada and also tracks West Nile Virus through human, mosquito, bird and horse surveillance. Link here to access their most current weekly update (reporting date June 21, 2021; retrieved July 29, 2021). The screenshot below (retrieved 29Jul2021) serves as a reference and reports one human case of WNV, a positive wild bird, and positive mosquito pools in Ontario.

Bird surveillance continues to be an important way to detect and monitor West Nile Virus. The Canadian Wildlife Health Cooperative (CWHC) works with governmental agencies (i.e., provincial laboratories and the National Microbiology Laboratory) and other organizations to report the occurrence of WNV. Dead birds retrieved from areas of higher risk of West Nile Virus are tested for the virus. A screenshot of the latest reporting results posted by Canadian Wildlife Health Cooperative is below (retrieved 29Jul2021).
Anyone keen to identify mosquitoes will enjoy this pictorial key for both larvae and adults which is posted on the Centre for Disease Control (CDC) website but sadly lacks a formal citation other than “MOSQUITOES: CHARACTERISTICS OF ANOPHELINES AND CULICINES prepared by Kent S. Littig and Chester J. Stojanovich” and includes Pages 134-150. The proper citation may be Stojanovich, Chester J. & Louisiana Mosquito Control Association. (1982). Mosquito control training manual. pp 152.