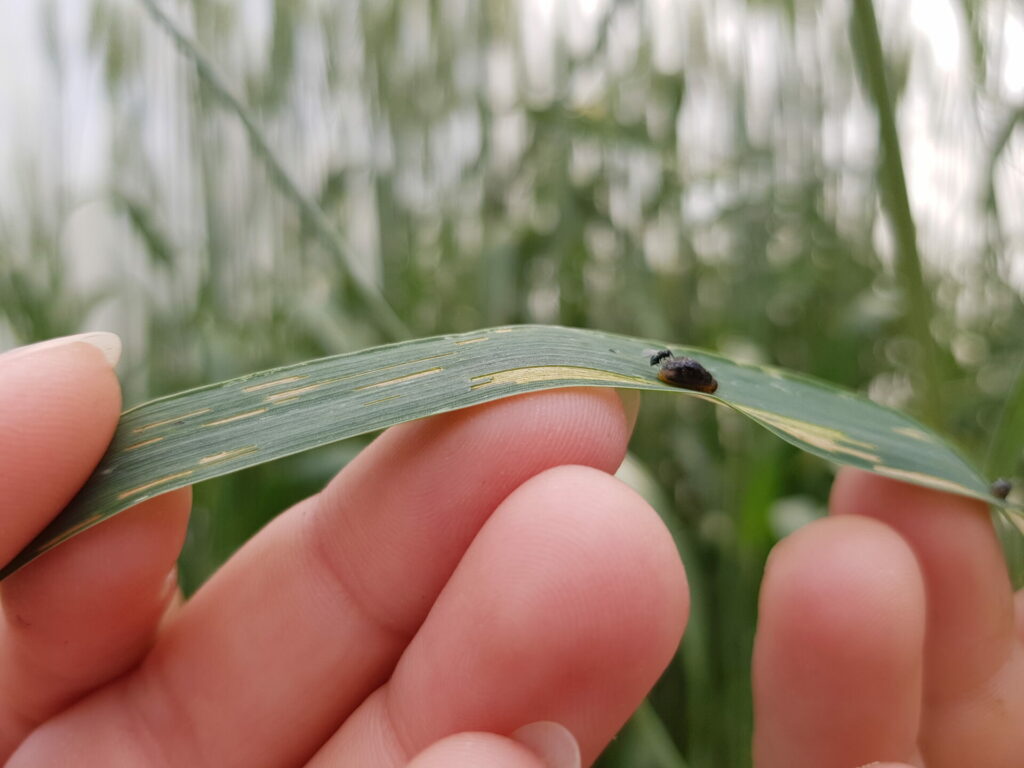
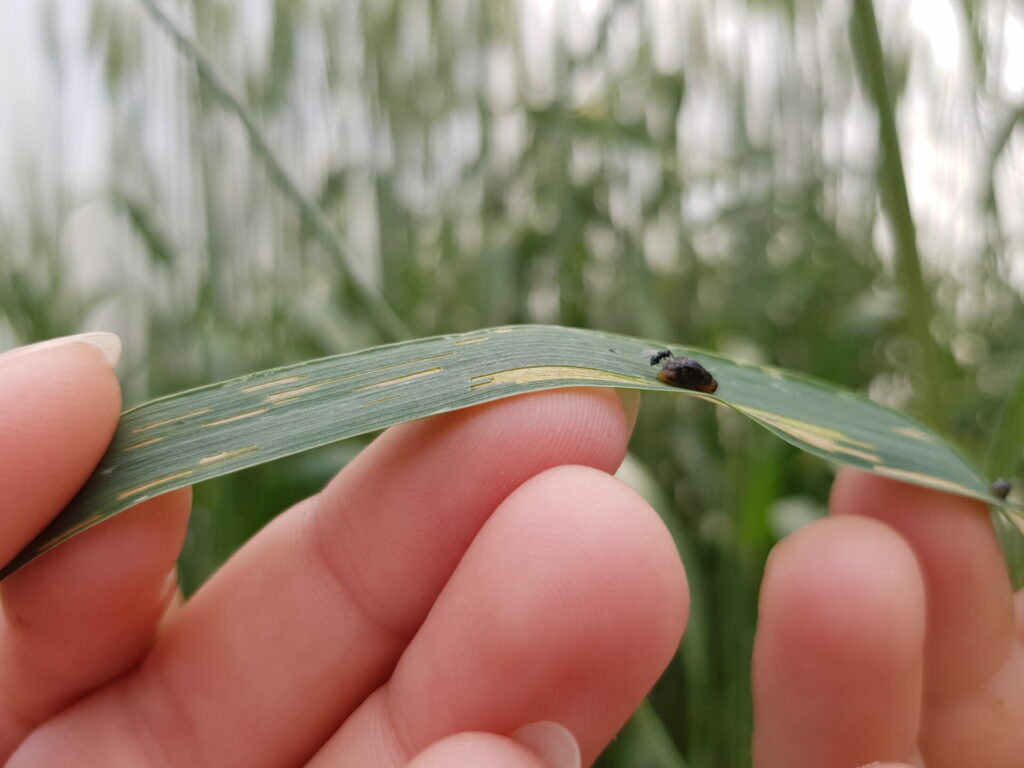
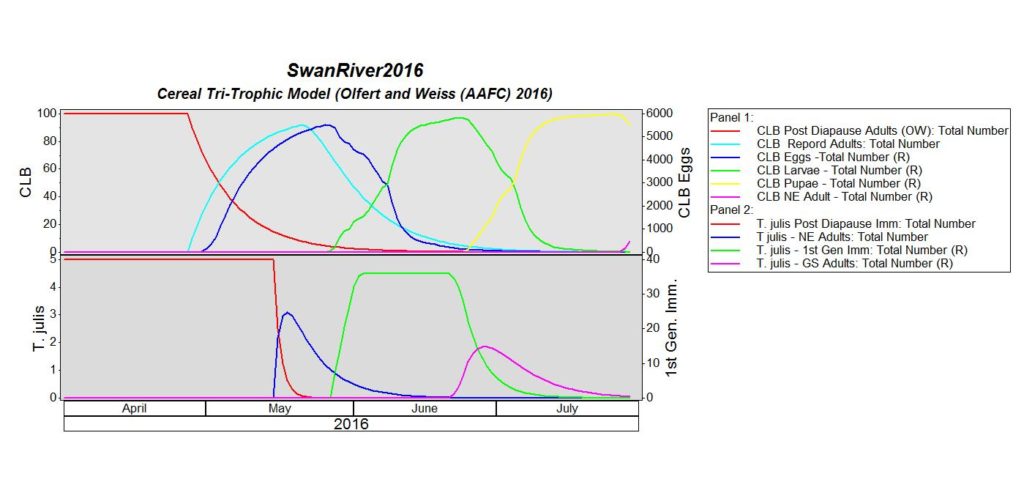
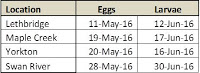
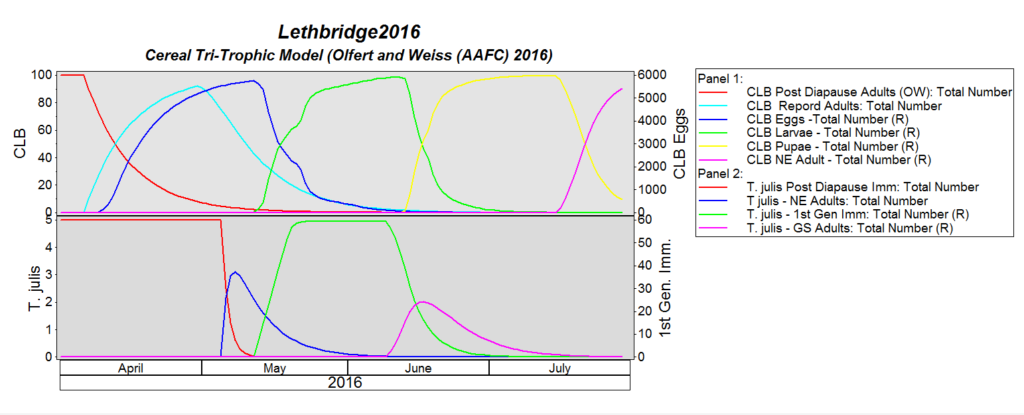
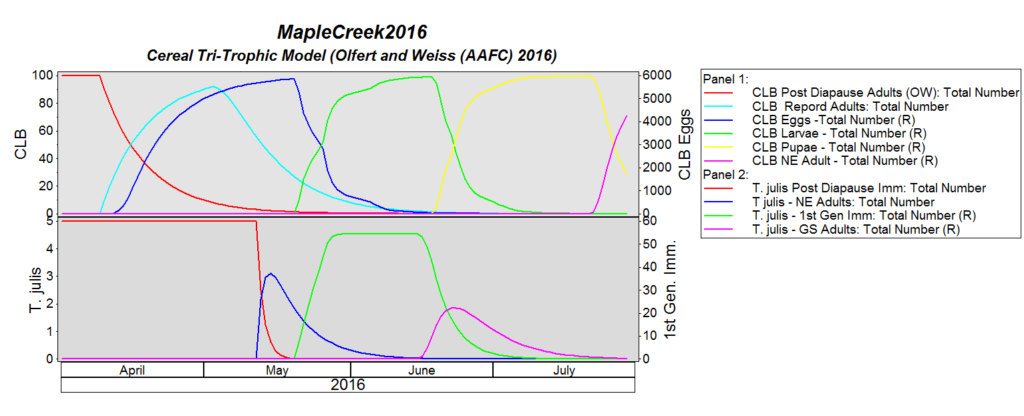
The cereal leaf beetle (Chrysomelidae: Oulema melanopus) has a broad host range. Wheat is the preferred host, but adults and larvae also feed on leaf tissue of oats, barley, corn, rye, triticale, reed canarygrass, ryegrass, fescue, wild oats, millet and other grasses. Yield quality and quantity is decreased, if the flag leaf is stripped. Fun fact: Cereal leaf beetle larvae carry their own fecal waste above their body to help protect themselves from predators.
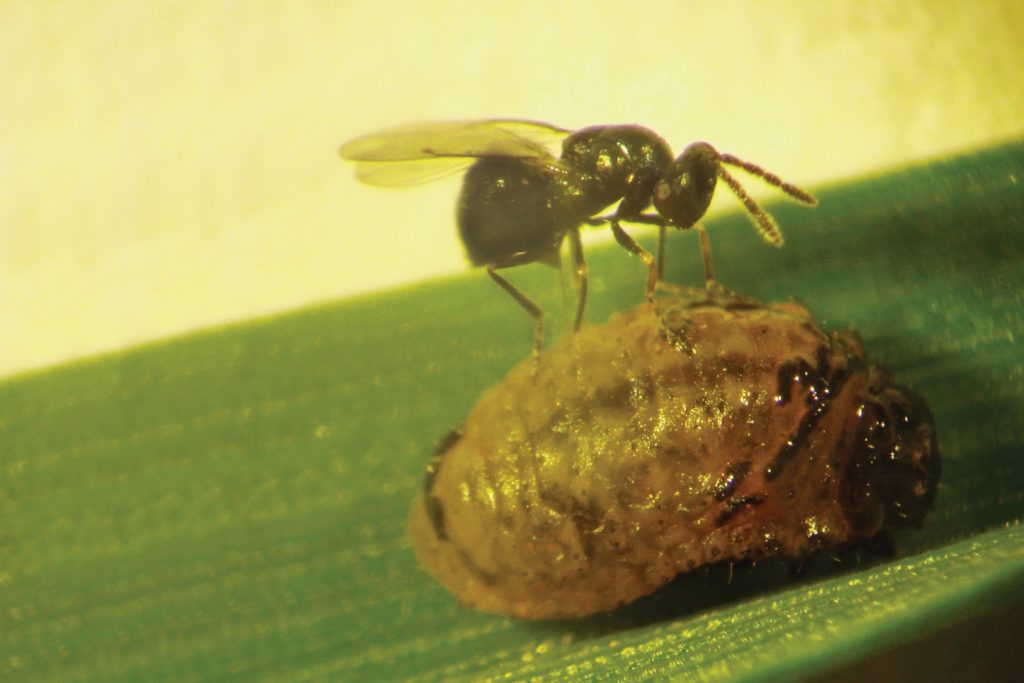
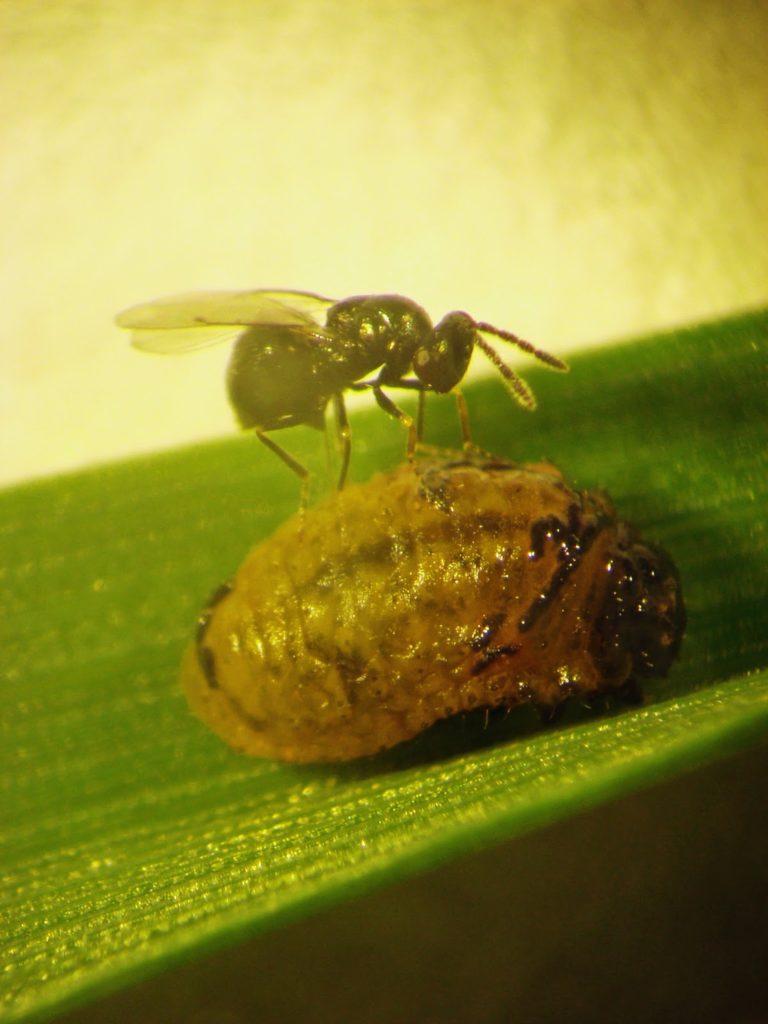
Fortunately, the parasitoid wasp, Tetrastichus julis Walker (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae), is an important natural enemy of cereal leaf beetle larvae. Learn more about this beneficial insect species featured in Week 9 of 2023’s Insect of the Week!
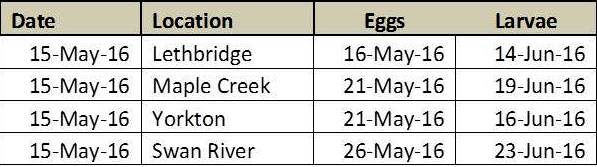
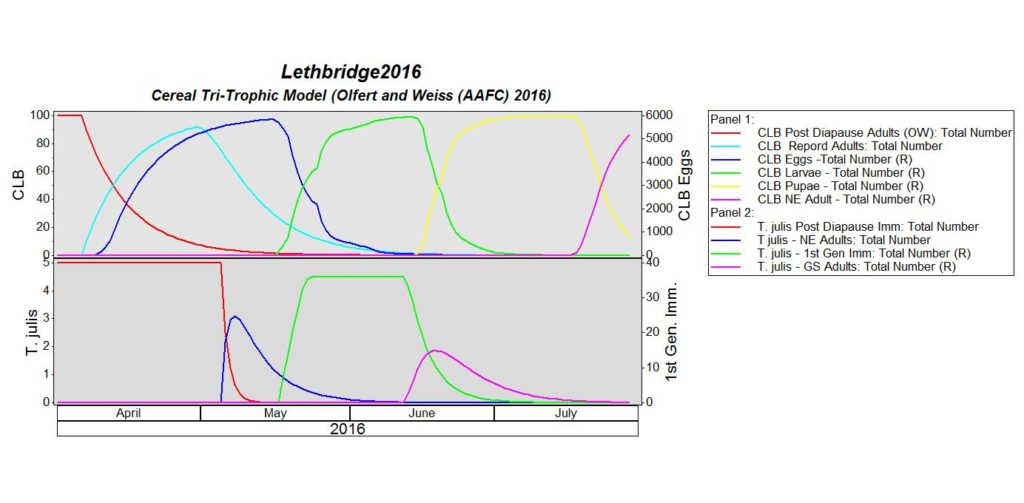
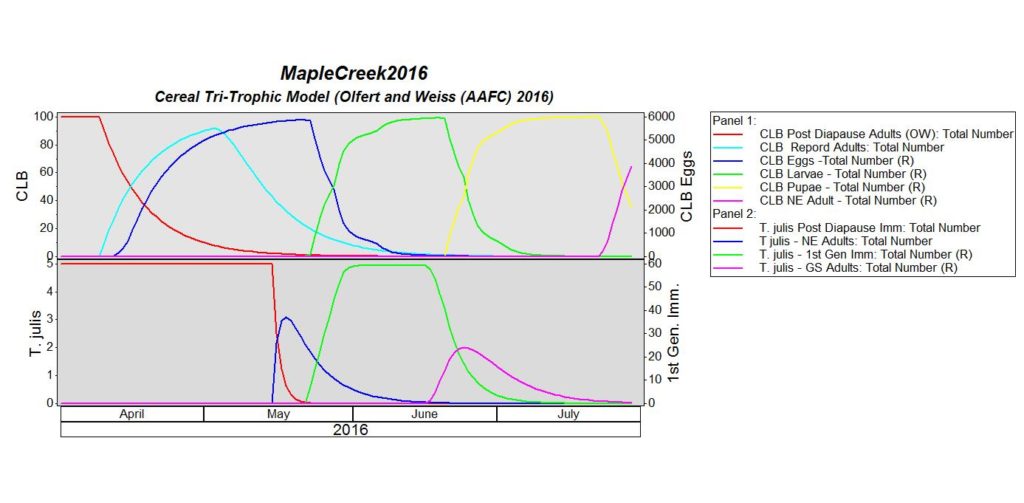
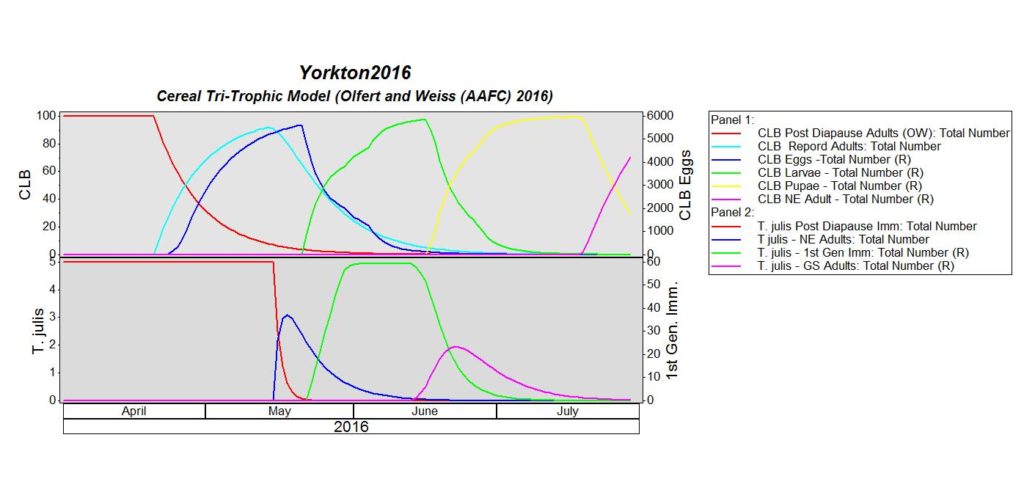
Cereal Leaf Beetle Lifecycle and Damage:
Adult: Adult cereal leaf beetles (CLB) have shiny bluish-black wing covers (Fig. 3). The thorax and legs are light orange-brown. Females (4.9 to 5.5 mm) are slightly larger than males (4.4 to 5 mm). Adult beetles overwinter in and along the margins of grain fields in protected places such as in straw stubble, under crop and leaf litter, and in the crevices of tree bark. They favour sites adjacent to shelterbelts, deciduous and conifer forests. They emerge in the spring once temperatures reach 10-15 ºC and the adults are active for about 6 weeks. They usually begin feeding on grasses, then move into winter cereals and later into spring cereals.

Egg: Eggs are laid approximately 14 days following the emergence of the adults. Eggs are laid singly or in pairs along the midvein on the upper side of the leaf and are cylindrical, measuring 0.9 mm by 0.4 mm, and yellowish in colour. Eggs darken to black just before hatching.
Larva: The larvae hatch in about 5 days and feed for about 3 weeks, passing through 4 growth stages (instars). The head and legs are brownish-black; the body is yellowish. Larvae are usually covered with a secretion of mucus and fecal material, giving them a shiny black, wet appearance (Fig. 4). When the larva completes its growth, it drops to the ground and pupates in the soil.

Pupa: Pupal colour varies from a bright yellow when it is first formed, to the colour of the adult just before emergence. The pupal stage lasts 2 – 3 weeks. Adult beetles emerge and feed for a couple of weeks before seeking overwintering sites. There is one generation per year.
Access scouting tips for cereal leaf beetle or find more detailed information by accessing the Oulema melanopus page from the “Field crop and forage pests and their natural enemies in western Canada – Identification and management field guide” (2018; accessible as a free downloadable PDF in either English or French on our new Field Guides page.