Prairie-wide provincial entomologists provide insect pest updates throughout the growing season. Follow the hyperlinks to readily access their information as the growing season progresses:
MANITOBA’S Crop Pest Updates for 2024 have started! Access the online May 23, 2024 report (or review a PDF copy). Bookmark the insect pest homepage to access fact sheets and more!
• Diamondback moth pheromone trap monitoring in MB – Dr. John Gavloski (Manitoba Agriculture) reported that, “Diamondback moth have been found in 55 out of 68 traps that counts were reported from. Trap counts have generally been low so far, however, some moderate counts have occurred in the Eastern, Interlake and Central regions. The highest cumulative trap count so far is 69 from a trap near Riverton in the Interlake region.”
• True armyworm in MB – Dr. John Gavloski (Manitoba Agriculture) reported that, “A network of pheromone-baited traps are being monitored at 34 locations from early-May until late-July to determine how early and in what levels populations of armyworms have arrive. Some moderate counts have occurred from traps in the Eastern and Interlake regions of Manitoba. The highest cumulative count is 76, from a trap near Riverton in the Interlake region.”
• Beneficial insect monitoring in MB – “Weekly monitoring of the levels and stages of five groups of
predaceous insects; lady beetles, green lacewings, hover flies, minute pirate bugs and damsel bugs”, will be undertaken using sweep-net sampling.
SASKATCHEWAN’S Crop Production News is back for the 2024 growing season! Access the online Issue #1 report. Bookmark their insect pest homepage to access important information!
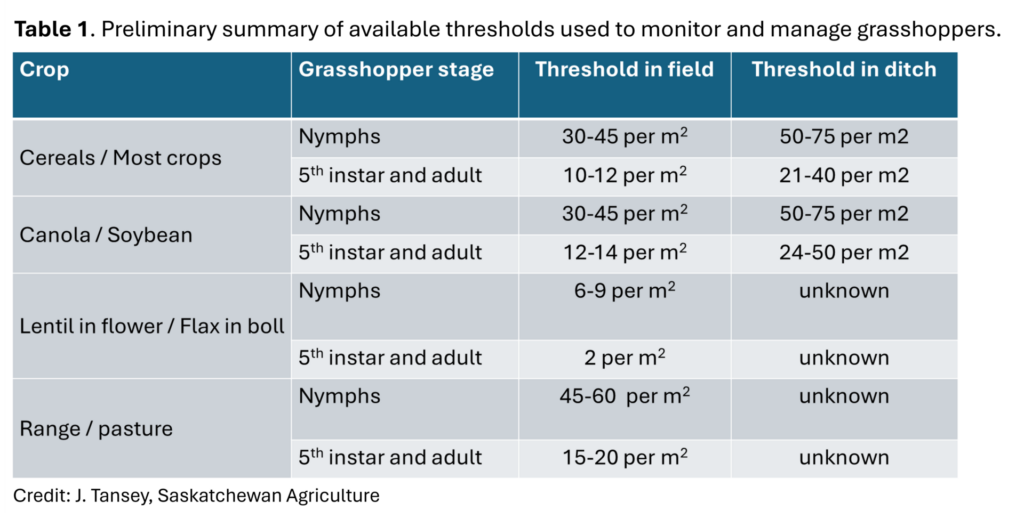
• Grasshopper hatch in SK – Updates that, ” eggs are being found by agrologists”, that “recent rains are unlikely to have a major impact on grasshopper populations”, that “nymphs have been found near OUtlook, Kindersley, and Regina”, and emphasizes the importance of “producers start(ing) to scout for eggs or nymphs”.
• Flea beetle monitoring in SK – Updates that, “fields in northern Saskatchewan have heavy flea beetle feeding on volunteer canola” and recommends, “producers across the province should frequently scout canola and mustard” following seedling emergence.
• Also access the Crops Blog Posts that announced registration for the Crop Diagnostic School 2024 but also posts help for scouting fields for wireworms (May 2024), grasshopper identification: pest or not (Apr 2024), a summary of wheat midge populations and management (Mar 2024), and a description of pea leaf weevil populations (Feb 2024).
ALBERTA’S Insect Pest Monitoring Network webpage links to insect survey maps, live feed maps, insect trap set-up videos, and more. There is also a Major Crops Insect webpage. Remember, AAF’s Agri-News occasionally includes insect-related information, e.g., flea beetle control (May 6, 2024); cereal insect pests, latest on insects in canola, and post-emergence wireworm scouting (May 13, 2024).
• Diamondback moth pheromone trap monitoring update for AB – Cumulative counts arising from weekly data are available so refer to the Live Map. So far, cumulative trap counts from the 29 reporting sites reflect low or “no risk” (as of May 23, 2024).
• Cutworm live monitoring map for AB – Cumulative counts arising from weekly data are available so refer to the Live Map. So far, 7 surveyed sites have reported from across the province and all are in southern Alberta.