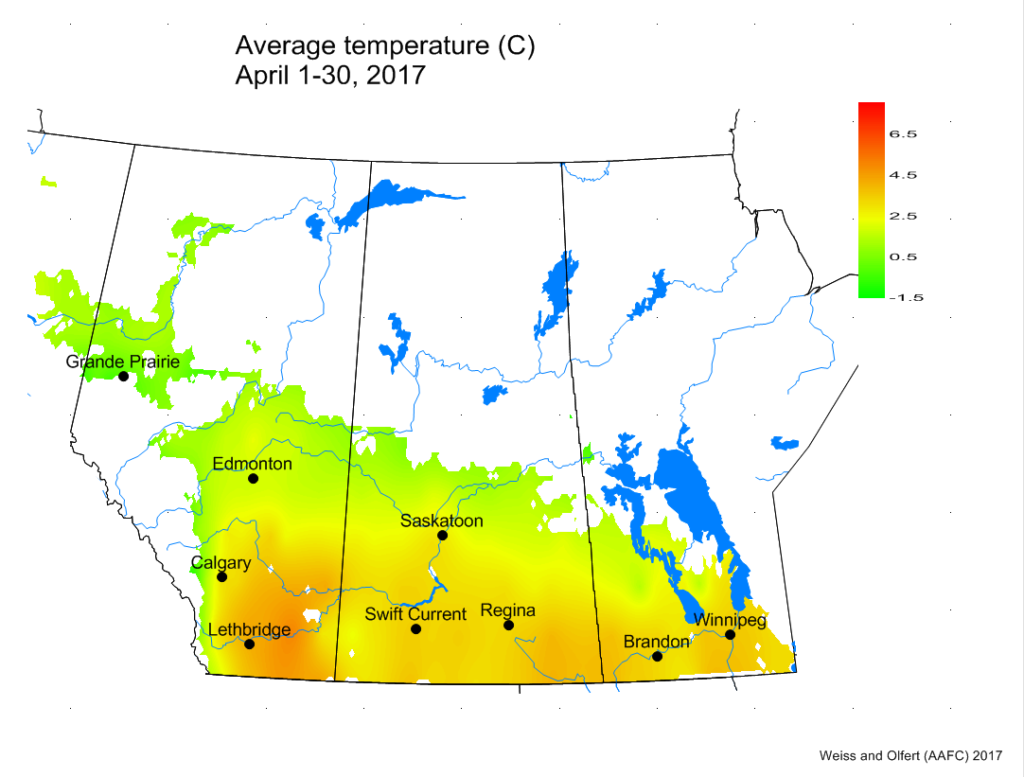
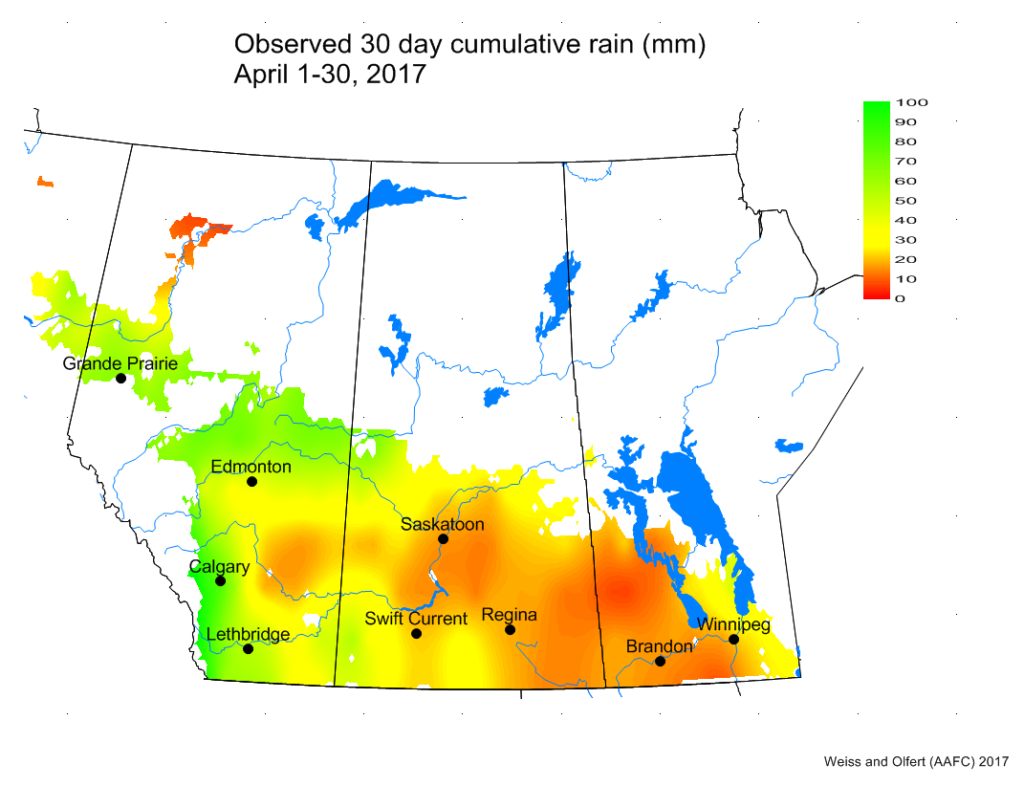
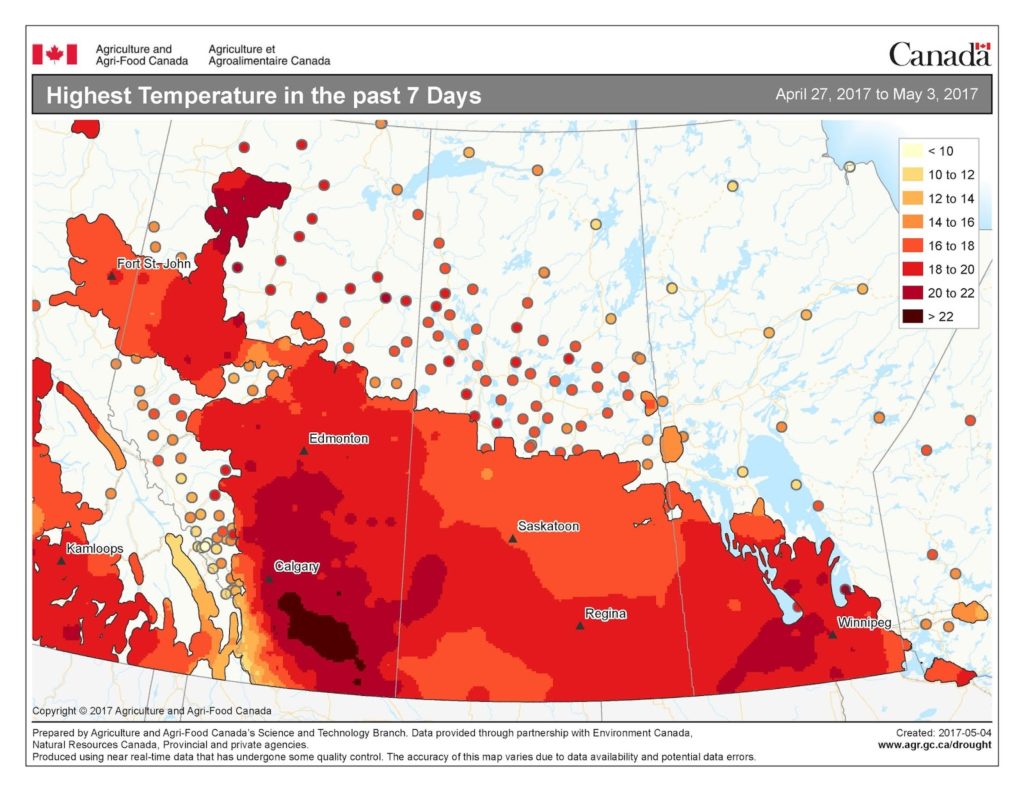
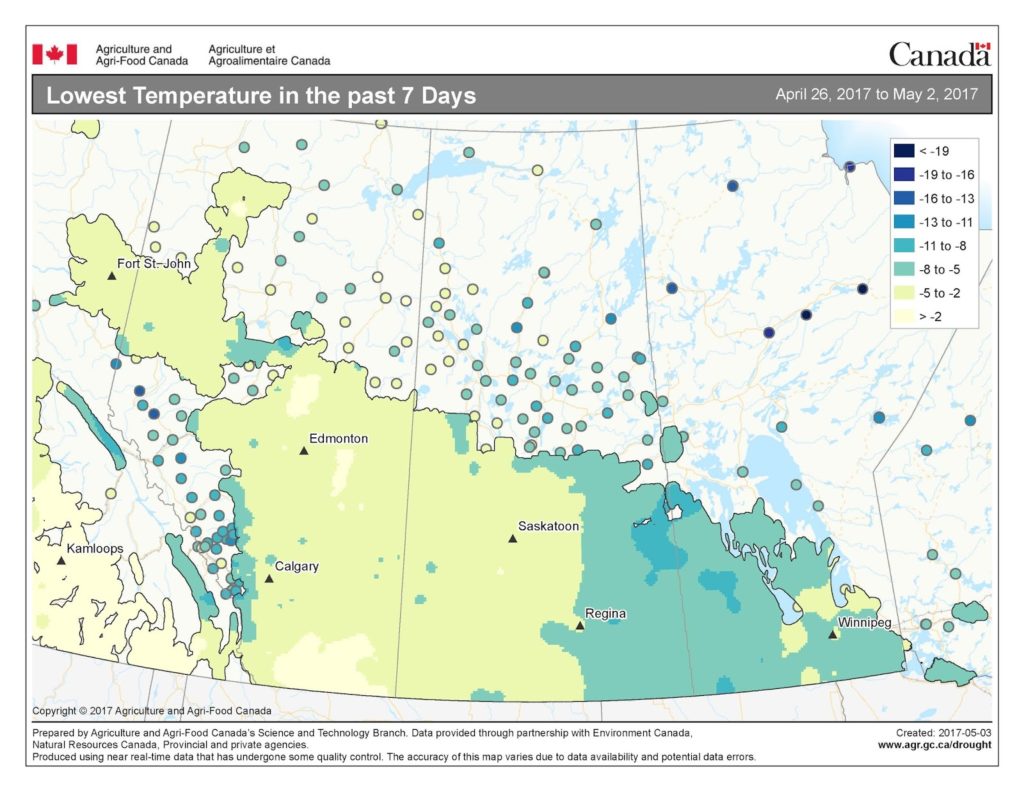
For many, seed isn’t even in the ground yet, but the cutworms are ready for it when it is. So the time to start scouting for cutworms is now! Even if it is too wet to seed, consider checking volunteer plants for cutworms or feeding damage. General cutworm monitoring protocols can be found on the Monitoring Protocols page. Species-specific protocols can be found in the new Cutworm Pests of Crops on the Canadian Prairies (see below for download details).
There are over 20 cutworm species that may cause economic damage to your crop, each with different feeding behaviour, preferred hosts and lifecycle. This is why species identification is so important: it helps growers understand what they are up against: determining how and when to scout, knowing whether the cutworm species is found above-ground (climbing) or below-ground, recognizing damage, choosing control options. Species also impacts the most appropriate time of day for monitoring and applying controls.
Action and economic thresholds do exist for many of the cutworm species – please use them. This will help control costs by eliminating unnecessary/un-economic sprays and reduce your impact on non-target insects – insects that include cutworm natural enemies that work in the background to control cutworm populations.
This week’s Insect of the Week is the Pale Western Cutworm. This is a below-ground feeder. Larvae hatch in late April/early May. As they feed on/tunnel through shoots as they pass through the soil, young larvae produce holes on newly-emerged shoots and furled leaves . Older larvae will sever plants just below the soil surface and may pull and eat the severed shoots underground.
For more information about Pale Western Cutworm, go to the Insect of Week page.
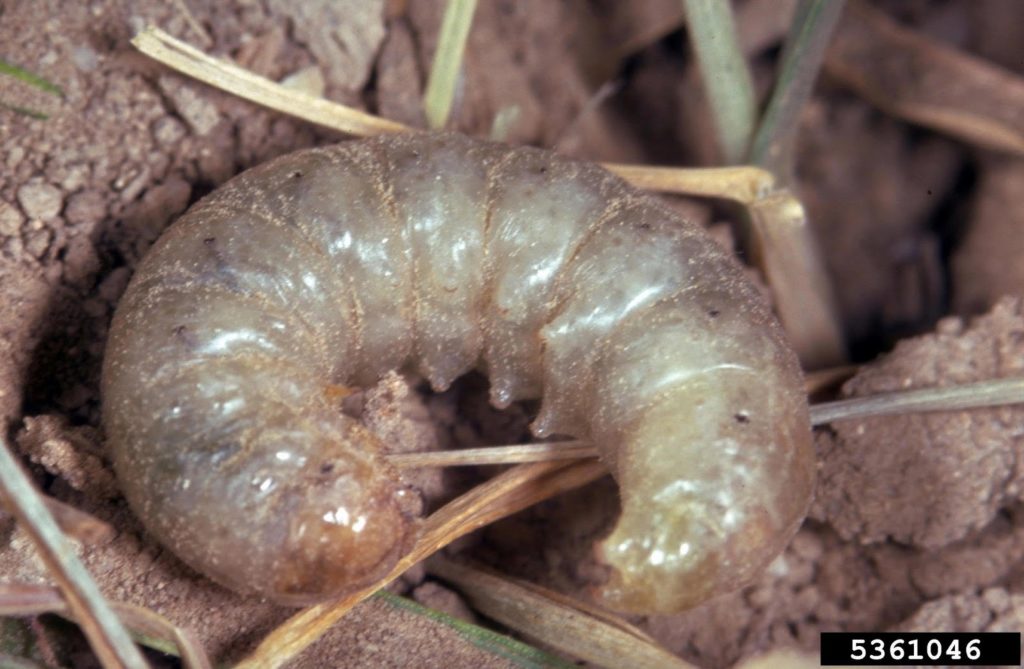 |
| Pale western cutwom. cc-by-nc 3.0 Frank Peairs, Colorado State University, bugwood.org |
Remember the NEW Cutworm Field Guide is free and downloadable in 2017!