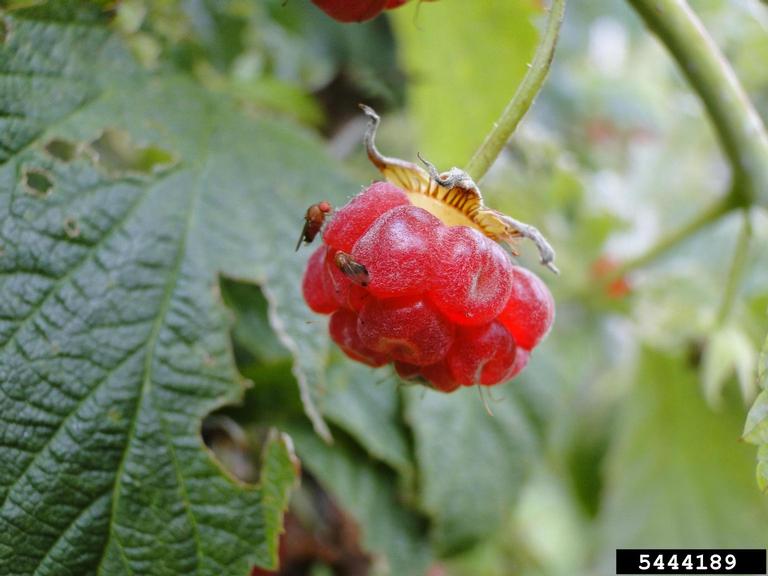
Spotted wing drosophila, Drosophila suzukii, is an invasive species that is now found in all 10 Canadian provinces. It was first confirmed to be present in British Columbia in 2009, Alberta in 2010, Manitoba in 2013, and Saskatchewan in 2019. It is still not as widespread in the prairie provinces as in other parts of Canada but is, unfortunately, becoming more common in the prairie region.
Spotted wing drosophila is a significant economic pest of fruits and berries. Unlike other fruit flies that are attracted to ripe or spoiling fruits and vegetables, spotted wing drosophila is capable of laying eggs in fresh, healthy fruits. It is a generalist and is known to feed on fruits in at least 19 plant families.

Adult spotted wing drosophila are small flies with light brown or dark yellow bodies. There are darker coloured bands on the abdomen and the eyes are dark red. Male flies have grey spots on their wingtips; the wings of female flies do not have spots.

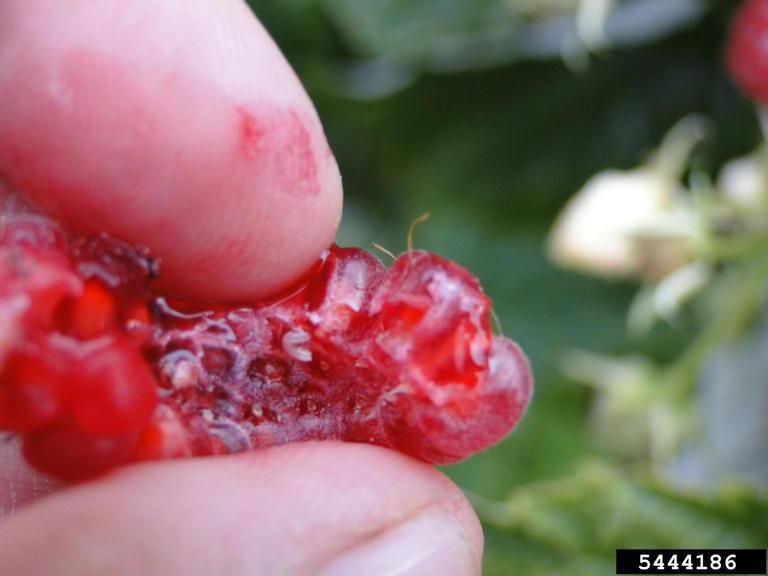
After mating, female flies use their saw-like ovipositor to slice into fresh fruit and then deposit 1-3 eggs into the fruit. Larve develop feeding inside the fruit, causing the fruit to spoil from the inside. It is often difficult to distinguish infested fruit from healthy fruit until after the fruit has been picked and cut open.
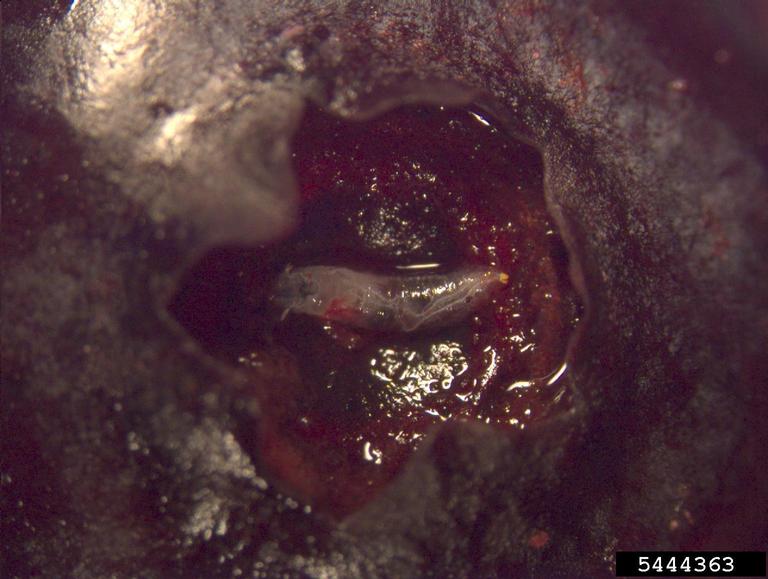
Managing spotted wing drosophila is challenging. Optimal methods for management of spotted wing drosophila in Canada, including biological control, are still being developed and tested. When picking fruit like raspberries and cherries on the prairies where spotted wing drosophila might be present, it is important to quickly clean and store the fruit in the fridge. Cold temperatures help to prevent eggs from hatching and will slow down larval development and feeding activity, helping to preserve infested fruit.
More spotted wing drosophila information (and pictures) is available from the CFIA, Manitoba Agriculture, Government of British Columbia, and the University of Minnesota Extension.





